Welcome to an interesting look into the world of gut health and the important role that legumes play in modulating gut inflammation. Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are not only a delicious addition to your meals, but they also contain high levels of fiber and antioxidants that can help promote a healthy gut microbiome. By incorporating more legumes into your diet, you may be able to reduce inflammation in your gut and improve overall digestive health. So next time you’re thinking about what to cook for dinner, consider adding some legumes for a tasty and gut-friendly option! Hey there! Have you ever wondered how legumes impact gut inflammation? Well, you’ve come to the right place! Let’s dive into the fascinating world of legumes and how they can help in modulating gut inflammation.
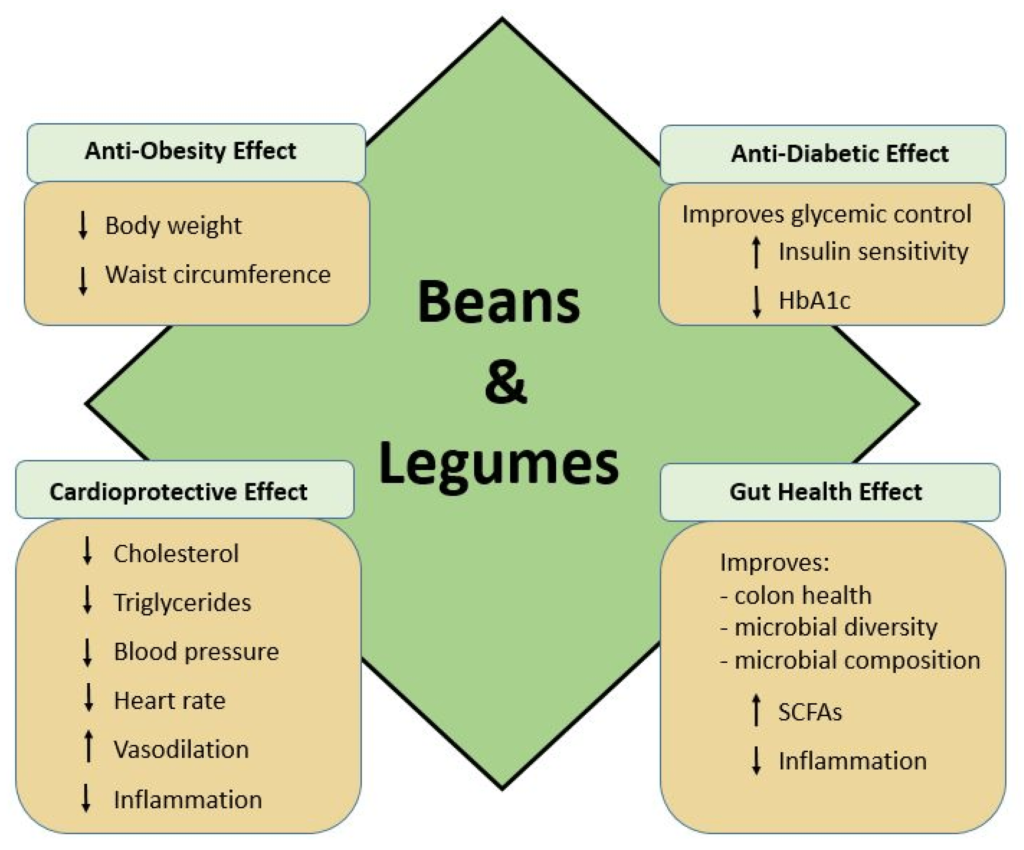
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
What are Legumes?
Legumes are a group of plants that produce pulses or seeds that are commonly consumed worldwide. They belong to the Fabaceae family and are known for their high protein and fiber content. Some common examples of legumes include beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas.
Legumes have been a staple in many cuisines for centuries due to their nutritional value and versatility in cooking. Whether you enjoy them in soups, salads, or stews, legumes can be a great addition to your diet.
Legumes are Nutrient-Rich Superfoods
Legumes are packed with essential nutrients that can benefit your overall health. They are an excellent source of plant-based protein, making them a great option for vegetarians and vegans. Additionally, legumes are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, such as iron, potassium, and folate.
By incorporating legumes into your diet, you can increase your intake of these vital nutrients, which are important for various bodily functions. So, next time you’re meal planning, consider including some legumes for a nutritious boost!
Gut Inflammation: Causes and Effects
Gut inflammation, also known as gastrointestinal inflammation, occurs when the lining of the digestive tract becomes inflamed. This inflammation can be caused by various factors, including poor diet, stress, infections, and certain medical conditions.
When the gut lining is inflamed, it can lead to a host of digestive issues, such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Chronic gut inflammation has also been linked to more serious conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Impact of Diet on Gut Inflammation
Your diet plays a significant role in the health of your gut. Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to gut inflammation. On the other hand, incorporating nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can help reduce inflammation and promote gut health.
By choosing foods that support a healthy gut, you can improve your digestion, boost your immune system, and reduce the risk of developing gastrointestinal disorders. So, let’s explore how legumes specifically can help in modulating gut inflammation.
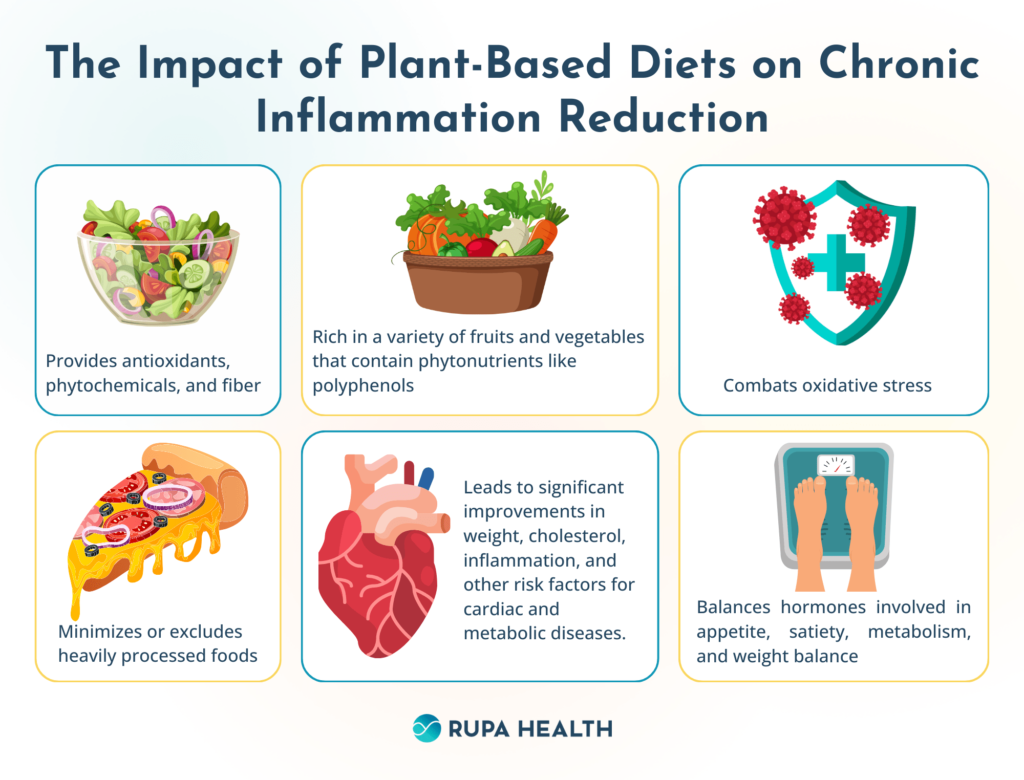
This image is property of cdn.prod.website-files.com.
How Legumes Help Modulate Gut Inflammation
Legumes contain a unique combination of nutrients and compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects in the body. These properties make legumes a valuable food for promoting gut health and reducing inflammation in the digestive tract.
High Fiber Content
One of the key ways in which legumes help modulate gut inflammation is through their high fiber content. Fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which is the community of beneficial bacteria that reside in your digestive system.
When you consume foods rich in fiber, such as legumes, it helps feed the good bacteria in your gut, which can improve digestion and reduce inflammation. Fiber also helps regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation, which can contribute to gut inflammation.
Rich in Polyphenols
Legumes are also rich in polyphenols, a group of plant compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Polyphenols help protect the gut lining from damage caused by free radicals and inflammatory processes.
By consuming legumes regularly, you can increase your intake of these beneficial polyphenols, which can help reduce gut inflammation and promote overall digestive health.
Source of Plant-Based Proteins
As mentioned earlier, legumes are an excellent source of plant-based proteins. Protein is essential for repairing and maintaining the tissues in your body, including the cells that line your digestive tract.
By including legumes in your diet, you can ensure that you’re getting an adequate amount of protein to support gut health and reduce inflammation. Plant-based proteins have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects in the body, making them a great addition to an anti-inflammatory diet.

This image is property of www.frontiersin.org.
Best Practices for Incorporating Legumes Into Your Diet
Now that you know how beneficial legumes can be for gut health, you may be wondering how to incorporate them into your daily meals. Here are some tips and best practices for adding more legumes to your diet:
Experiment with Different Varieties
There are many types of legumes available, each with its own unique flavor and texture. Experiment with different varieties, such as black beans, chickpeas, lentils, and edamame, to find the ones you enjoy the most.
Try adding chickpeas to salads, making lentil soup, or using black beans in tacos. The possibilities are endless when it comes to incorporating legumes into your meals!
Use Legume-based Flours and Pastas
If you’re looking for gluten-free alternatives or want to increase your legume intake, consider using legume-based flours and pastas. Chickpea flour, lentil flour, and black bean pasta are excellent options that can add a nutritional boost to your dishes.
You can use these alternatives in baking, cooking, and meal prep to enjoy the benefits of legumes in a convenient and versatile way.
Include Legumes in Meatless Meals
If you’re trying to reduce your meat consumption or follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, legumes can be a great alternative to animal proteins. Use beans, lentils, or tofu in place of meat in recipes such as chili, stir-fries, and tacos.
Including more meatless meals in your diet can not only benefit your health but also help support sustainable food choices and reduce your environmental impact.

This image is property of images.everydayhealth.com.
Potential Side Effects of Legumes
While legumes offer a multitude of health benefits, some individuals may experience digestive issues when consuming them. This is due to compounds found in legumes, such as oligosaccharides, which can be difficult for some people to digest.
Gas and Bloating
One common side effect of eating legumes is gas and bloating. This is often caused by the fermentation of indigestible carbohydrates in legumes by gut bacteria, which produces gas as a byproduct.
If you experience gas and bloating after eating legumes, try soaking them before cooking or gradually increasing your intake to help your body adjust. You can also try cooking legumes with aromatics like garlic, ginger, and cumin to aid digestion.
Antinutrients
Legumes contain compounds known as antinutrients, such as phytates and lectins, which can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals in the body. While antinutrients have some health benefits, they can be problematic for individuals with nutrient deficiencies.
To reduce the effects of antinutrients in legumes, you can soak, sprout, or ferment them before cooking. These methods can help break down antinutrients and improve the bioavailability of nutrients in legumes.
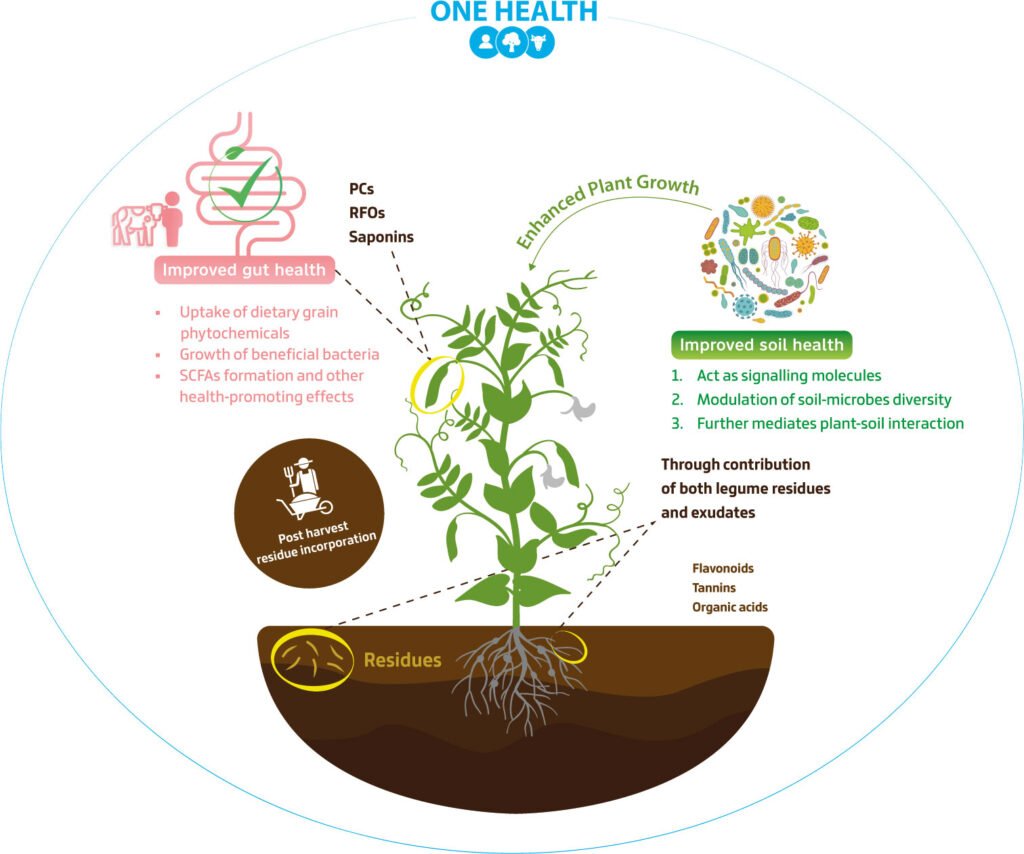
This image is property of www.frontiersin.org.
Conclusion
In conclusion, legumes play a crucial role in modulating gut inflammation due to their high fiber content, polyphenol content, and plant-based protein content. By including legumes in your diet, you can promote a healthy gut microbiome, reduce inflammation in the digestive tract, and support overall digestive health.
Remember to experiment with different varieties of legumes, use legume-based flours and pastas, and include legumes in meatless meals to reap the benefits of these nutrient-rich superfoods. While some individuals may experience digestive issues when consuming legumes, there are strategies to help mitigate these effects and enjoy the health benefits of legumes.
So, next time you’re at the grocery store, why not pick up some chickpeas, lentils, or black beans and get creative in the kitchen? Your gut will thank you for it!

