Have you ever wondered how whole grains can help you feel fuller for longer and assist with managing your weight? In the context of gut health, whole grains play an important role in promoting satiety and aiding in weight management. By providing a good amount of dietary fiber, whole grains help regulate digestion, keep you feeling satisfied, and may even contribute to reducing the risk of certain chronic conditions. Let’s explore the fascinating connection between whole grains, satiety, weight management, and gut health in this article.
What are whole grains?
Definition of whole grains
Whole grains are cereal grains that contain all parts of the grain kernel – the bran, germ, and endosperm. Unlike refined grains, which have been processed to remove the bran and germ, whole grains retain the full nutritional value. They are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a valuable component of a healthy diet.
Examples of whole grains
There is a wide variety of whole grains to choose from, including:
- Brown rice
- Whole wheat
- Oats
- Barley
- Quinoa
- Buckwheat
- Millet
- Amaranth
These grains can be incorporated into meals in various ways, such as in the form of bread, pasta, cereals, or as a side dish.
Nutritional composition of whole grains
Whole grains provide a range of essential nutrients, including:
- Fiber: Whole grains are a rich source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion, promotes satiety, and supports a healthy gut.
- Protein: They contain a moderate amount of protein, which is important for building and repairing body tissues.
- Vitamins and minerals: Whole grains are an excellent source of vitamins B and E, as well as minerals like iron, magnesium, and selenium.
- Antioxidants: These grains are packed with antioxidants, which help protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation.
Including whole grains in your diet can provide a wide array of nutrients that are beneficial for overall health and well-being.
What is satiety and its role in weight management?
Definition of satiety
Satiety refers to the feeling of fullness and satisfaction after eating a meal. It is a complex physiological response that involves sensory, hormonal, and neural signals. When we feel satiated, we are less likely to overeat or snack between meals, which can play a significant role in weight management.
Factors influencing satiety
Several factors influence satiety, including:
- Macronutrient composition: Meals rich in protein and fiber tend to be more satiating than those high in refined carbohydrates or unhealthy fats.
- Volume and density: Foods that have a higher volume or density, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, often promote greater satiety.
- Eating rate: Eating slowly and mindfully allows time for the brain to receive signals of fullness from the gut, contributing to feelings of satiety.
- Hormonal regulation: Hormones involved in appetite control, such as leptin and ghrelin, play a role in determining satiety levels.
Importance of satiety in weight management
Satiety is crucial for weight management because it helps regulate energy intake. By choosing foods that promote satiety, we can feel satisfied with fewer calories, which can lead to weight loss or maintenance. Whole grains, with their high fiber content and ability to create a feeling of fullness, can be a valuable tool in promoting satiety and supporting a healthy weight.

This image is property of media.post.rvohealth.io.
Understanding gut health
What is gut health?
Gut health refers to the optimal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the balance of microorganisms, known as gut microbiota, within it. A healthy gut is vital for digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and overall well-being. It plays a significant role in various aspects of our health, including mental health, immune system regulation, and even weight management.
Importance of gut health in overall well-being
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being. A healthy gut:
- Supports optimal digestion: A well-functioning gut ensures proper breakdown and absorption of nutrients, maximizing their benefits for the body.
- Boosts immune function: The gut is home to a large portion of our immune system, and a healthy gut plays a crucial role in defending against harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
- Affects mental health: The gut and the brain are intricately connected through the gut-brain axis. A healthy gut can contribute to better mental health and mood regulation.
- Influences systemic inflammation: Imbalances in the gut microbiota can lead to chronic inflammation, which is associated with various health issues, including obesity and metabolic syndrome.
The role of gut microbiota in gut health
The gut microbiota, consisting of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, is essential for gut health. These microorganisms help break down dietary fiber, produce certain vitamins, and compete with harmful bacteria. They contribute to the maintenance of a healthy gut environment and play a crucial role in nutrient absorption and immune system regulation.
The link between whole grains and satiety
Fiber content of whole grains
One of the key factors that contribute to the satiating effect of whole grains is their high fiber content. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is not digested by the body. Instead, it passes through the digestive system relatively intact, adding bulk to the stool and promoting feelings of fullness.
Effect of fiber on satiety
The fiber found in whole grains absorbs water and expands in the stomach, creating a feeling of fullness and reducing appetite. It also slows down the rate at which food moves through the digestive system, prolonging the release of hunger-suppressing hormones and promoting feelings of satiety.
Mechanisms behind the satiating effect of fiber
Several mechanisms contribute to the satiating effect of fiber found in whole grains:
- Delayed gastric emptying: Fiber slows down the emptying of the stomach, leading to a slower release of nutrients into the small intestine and a prolonged feeling of fullness.
- Increased production of gut hormones: Fiber stimulates the production of various hormones involved in appetite regulation, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY), which signal the brain that you are full.
- Improved microbiota diversity: Fiber serves as a prebiotic, providing nourishment to beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiota composition is associated with enhanced satiety signals.
Including whole grains in your diet can help increase your fiber intake and promote feelings of satiety, making it easier to manage your weight.
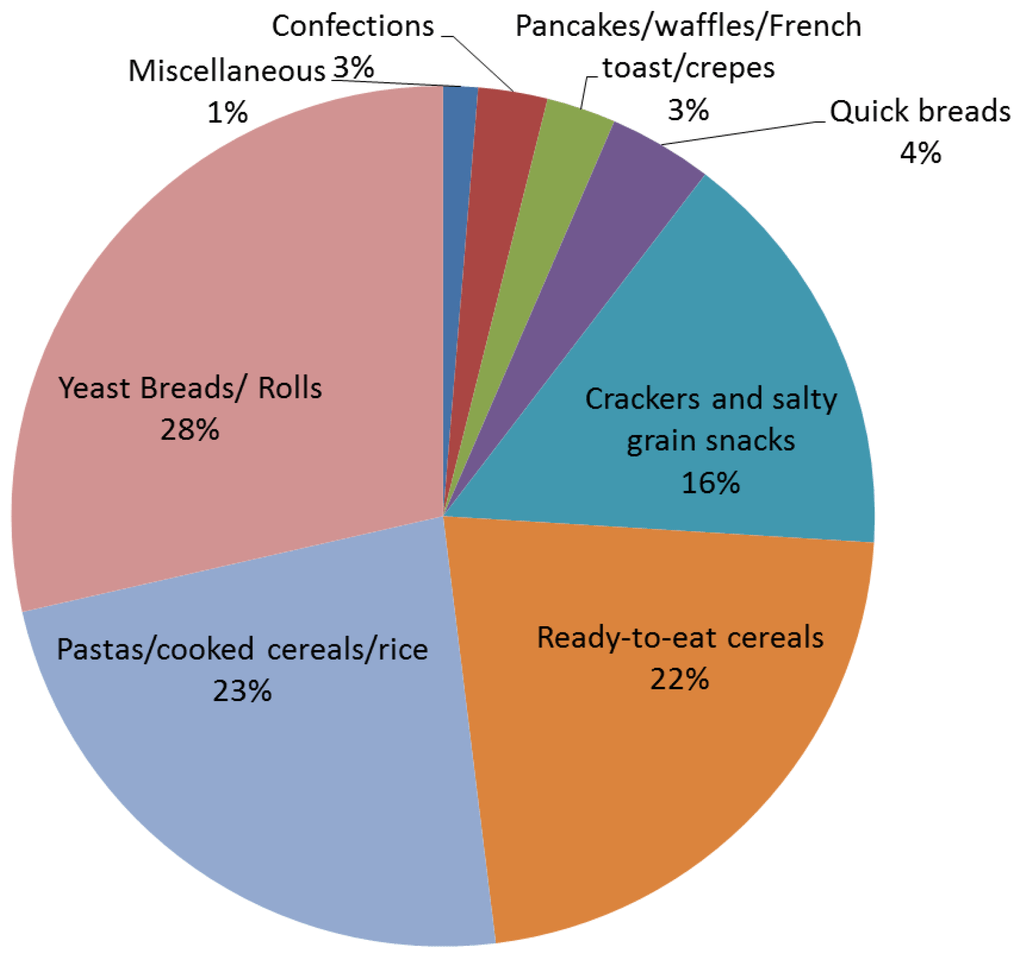
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
The impact of whole grains on weight management
Whole grains and energy balance
Whole grains can contribute to weight management by helping to maintain a healthy energy balance. Energy balance refers to the relationship between the energy consumed through food and the energy expended through physical activity and bodily functions. Whole grains are nutrient-dense and generally lower in calories compared to refined grains, making them a more satisfying and weight-friendly choice.
Role of whole grains in reducing calorie intake
Whole grains have a higher satiety value compared to refined grains, meaning they can help you feel fuller with fewer calories. By including whole grains in your meals, you can reduce the overall calorie intake without sacrificing satisfaction or taste.
Effect of whole grains on metabolism
The complex carbohydrates and fiber found in whole grains require more energy to digest compared to refined carbohydrates. This is known as the thermic effect of food, where the body burns calories during the digestion process. By incorporating whole grains into your diet, you can slightly increase your metabolic rate and potentially support weight management efforts.
Whole grains and gut health
Whole grains as prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible food components that stimulate the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Whole grains, particularly those high in fiber, can act as prebiotics, promoting the growth of specific strains of bacteria that contribute to a healthy gut environment.
Effect of whole grains on gut microbiota
The fiber in whole grains acts as a fuel source for bacteria in the gut, allowing them to thrive and perform their beneficial functions. Whole grains support the growth of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which are associated with improved gut health and immune function. A diverse and balanced gut microbiota is essential for maintaining gut health and overall well-being.
Promotion of a healthy gut environment by whole grains
Whole grains provide a nourishing environment for gut bacteria and support the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate. SCFAs are essential for a healthy gut, as they provide energy for colon cells, reduce inflammation, and enhance the integrity of the gut barrier. By consuming whole grains, you can support the growth of beneficial bacteria and promote a healthy gut environment.
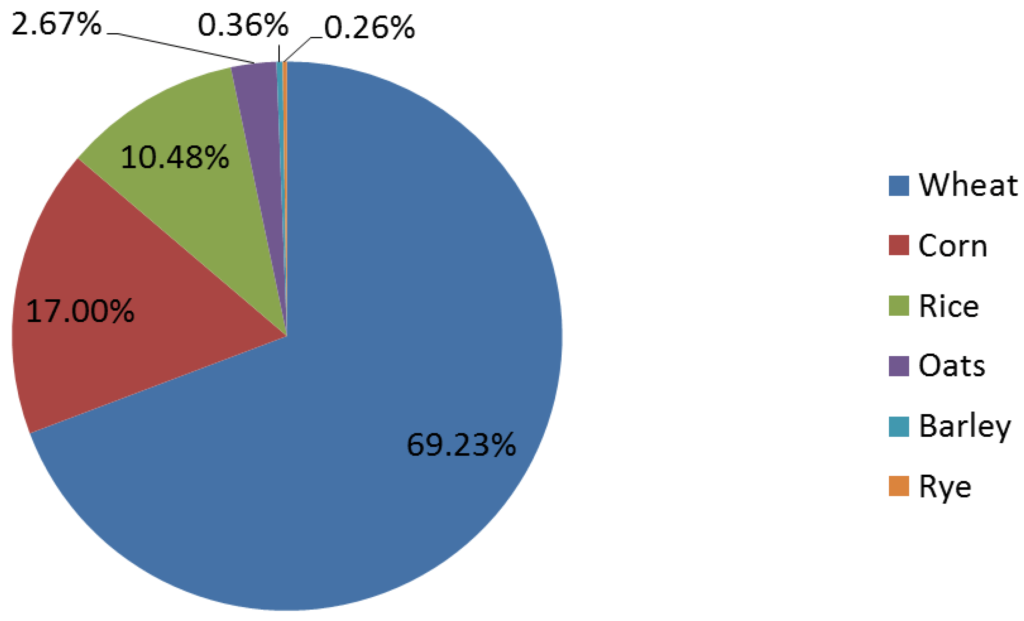
This image is property of pub.mdpi-res.com.
The role of gut health in weight management
Impact of gut health on metabolism
A healthy gut plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, the process by which the body converts food into energy. Imbalances in the gut microbiota composition and increased intestinal permeability, also known as “leaky gut,” can contribute to metabolic dysregulation and weight gain. By maintaining a healthy gut, you can support a more efficient metabolism and potentially aid in weight management.
Association between gut dysbiosis and obesity
Gut dysbiosis, characterized by an imbalance in the gut bacteria composition, has been linked to obesity. Studies have found that individuals with obesity tend to have a less diverse gut microbiota, with an overrepresentation of certain bacteria associated with weight gain. Improving gut health through the consumption of whole grains and other fiber-rich foods can help restore a healthy gut microbiota and potentially aid in weight management.
How improving gut health can aid in weight management
By improving gut health, you can enhance your body’s ability to regulate appetite, metabolism, and energy balance. Consuming whole grains, which promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, can support a healthier gut microbiota. This can result in improved digestion, enhanced nutrient absorption, and better control over food cravings, ultimately contributing to weight management efforts.
Recommended intake of whole grains
Current dietary guidelines
The current dietary guidelines recommend consuming at least half of all grains as whole grains. This equates to roughly three to five servings of whole grains per day, depending on age, sex, and activity level. A serving of whole grains is typically equivalent to one slice of whole wheat bread, ½ cup of cooked whole grain pasta or rice, or one ounce of whole grain cereal.
Factors to consider when choosing whole grain products
When selecting whole grain products, it is essential to read food labels and look for key indicators of whole grain content. Look for terms like “100% whole grain,” “whole wheat,” or “whole grain [name of grain].” Avoid products that list refined grains, such as enriched flour or degerminated cornmeal, as primary ingredients. Adding a variety of whole grains to your diet can provide different flavors and a broader range of nutrients.

This image is property of i.dietdoctor.com.
Tips for incorporating more whole grains into the diet
Choosing whole grain options
When grocery shopping, opt for whole grain versions of your favorite foods, such as whole grain bread, pasta, and cereals. Experiment with different types of whole grains, like quinoa, brown rice, or buckwheat, to add variety to your diet. Don’t forget to check food labels carefully to ensure you are selecting products that truly contain whole grains.
Replacing refined grains with whole grains
Gradually replace refined grains with whole grains in your meals. For example, instead of white rice, choose brown rice. Swap white bread for whole grain bread when making sandwiches. These simple substitutions can significantly increase your whole grain intake over time without sacrificing taste or enjoyment.
Trying new whole grain recipes
Explore new recipes that showcase the deliciousness of whole grains. Try making dishes like a colorful quinoa salad, a hearty barley soup, or a flavorful whole grain pilaf. By incorporating whole grains into your favorite recipes or experimenting with new ones, you can discover exciting and satisfying ways to enjoy these nutritious foods.
Conclusion
Incorporating whole grains into your diet can have numerous benefits for satiety, weight management, and gut health. Whole grains are nutritious, rich in fiber, and contribute to feelings of fullness, making them a valuable tool for weight management. They also promote a healthy gut environment by acting as prebiotics and supporting a diverse gut microbiota. A healthy gut, in turn, can aid in weight management and overall well-being. By following current dietary guidelines and incorporating whole grains into your meals, you can harness the power of these foods to optimize your health and enjoy a well-rounded and satisfying diet. So make a conscious effort to include whole grains in your meals and reap the benefits they offer for satiety, weight management, and gut health.
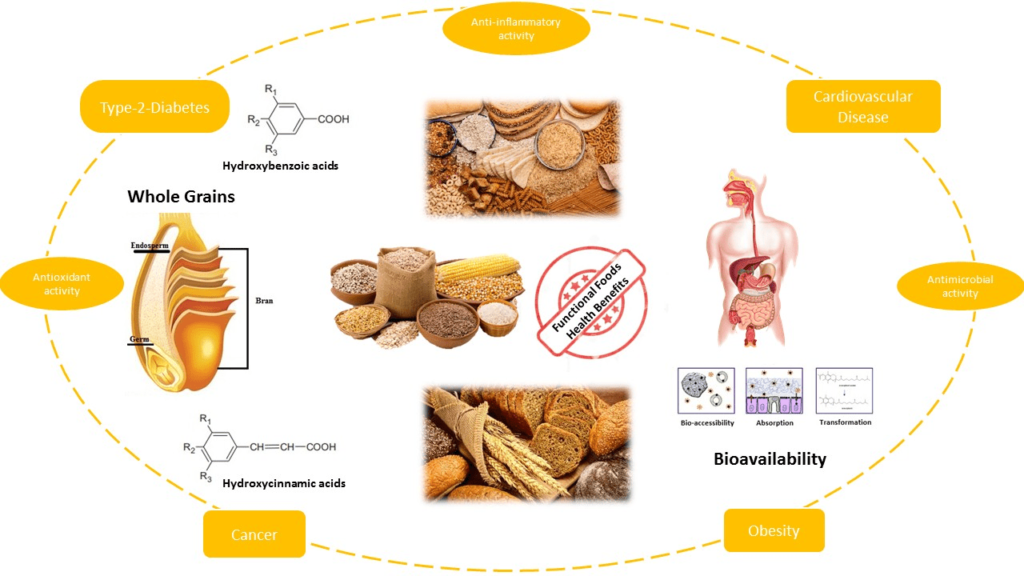
This image is property of pub.mdpi-res.com.
