Did you know that whole grains might have more to offer than just fiber and nutrients? Recent research suggests that they may also play a role in promoting gut health by containing anti-inflammatory compounds. These compounds have the potential to reduce inflammation in the gut, improving digestion and overall well-being. So, the next time you reach for a slice of whole grain bread or a bowl of whole grain cereal, you may be doing your gut a favor!

This image is property of content.health.harvard.edu.
Understanding Whole Grains
Definition of whole grains
Whole grains are the seeds or kernels of plants that contain all three parts of the grain: the bran, germ, and endosperm. Unlike refined grains, which have had the bran and germ removed, whole grains retain these nutrient-rich components, making them a healthier choice. Examples of whole grains include wheat, oats, barley, brown rice, quinoa, and corn.
Benefits of consuming whole grains
Including whole grains in your diet can have numerous benefits for your overall health. They are packed with essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support healthy digestion, weight management, heart health, and even reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer. Additionally, whole grains have been found to have anti-inflammatory and gut health benefits, which we will explore further in this article.
Types of whole grains
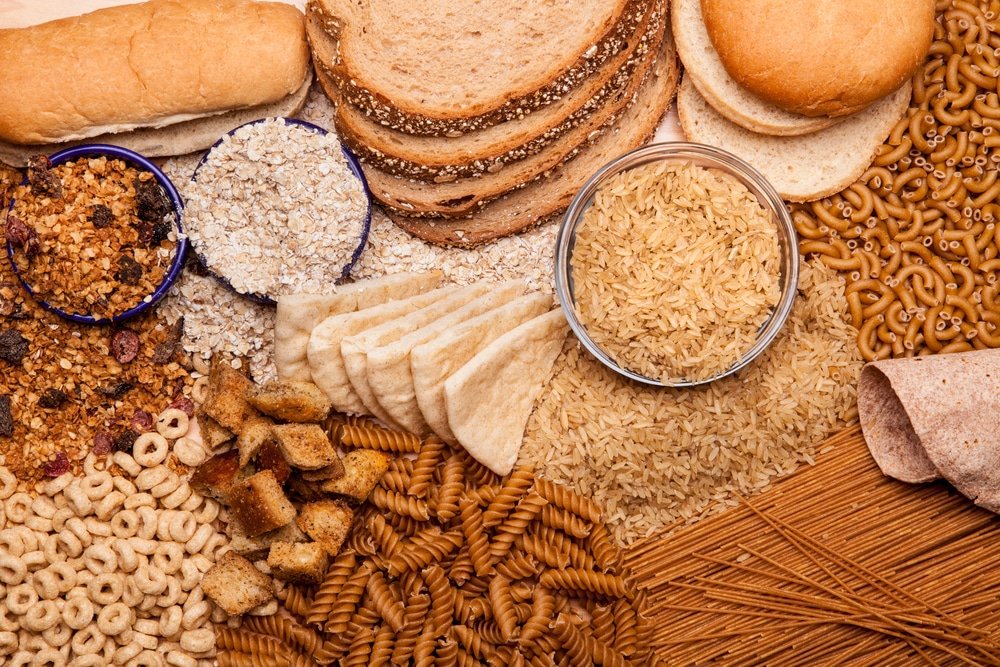
Whole grains come in many different varieties, each with their own unique nutritional profile and taste. Some common types of whole grains include:
- Wheat: A versatile grain used in a wide range of products, including bread, pasta, and cereals.
- Oats: Known for their high fiber content and often enjoyed as oatmeal or in granola bars.
- Barley: A grain that adds a nutty flavor to soups, stews, and salads.
- Brown rice: A whole grain alternative to white rice, rich in fiber and nutrients.
- Quinoa: A complete protein source that can be cooked and used as a base for salads or side dishes.
- Amaranth: A gluten-free grain with a slightly sweet and nutty flavor often used in porridges or as a flour substitute.
- Buckwheat: Despite the name, it is not related to wheat and is often ground into flour for making pancakes or noodles.
- Millet: A small grain used in various dishes, including pilafs, porridges, and bread.
- Rye: Often found in bread and crackers, rye has a unique flavor and is rich in fiber and antioxidants.
- Corn: A popular grain used in a variety of forms, such as cornmeal, popcorn, and tortillas.
Anti-Inflammatory Compounds in Whole Grains
Introduction to anti-inflammatory compounds
Anti-inflammatory compounds are substances that help reduce inflammation in the body, which is a natural response to injury or infection but can become chronic and detrimental to health. These compounds work by inhibiting the production of inflammatory molecules, balancing the immune response, and promoting tissue repair.
Research on anti-inflammatory compounds in whole grains
Several studies have highlighted the presence of anti-inflammatory compounds in whole grains. These compounds have been found to have protective effects against various chronic diseases associated with inflammation, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The diverse and complex array of bioactive compounds present in whole grains are believed to contribute to these anti-inflammatory effects, making them a valuable addition to a gut-healthy diet.
Various types of anti-inflammatory compounds found in whole grains
Whole grains contain a range of bioactive compounds with anti-inflammatory properties. Some of the key anti-inflammatory compounds found in whole grains include:
- Phenolic acids: Found in high amounts in whole wheat and oats, these compounds have been shown to inhibit inflammatory pathways in the body and protect against chronic inflammation.
- Flavonoids: Abundant in a variety of whole grains, flavonoids have been associated with reduced inflammation and improved gut health.
- Lignans: Found in foods like flaxseed, lignans have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects and may also have hormonal and antioxidant benefits.
- Phytoestrogens: Certain whole grains, such as oats and barley, contain phytoestrogens that have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties.
- Tocotrienols: A type of vitamin E found in whole grains, tocotrienols have been found to have anti-inflammatory effects and protect against oxidative stress.
Impact on Gut Health
Importance of gut health
The gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. A healthy gut is essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, mood regulation, and even cognitive function. Imbalances in the gut microbiota and chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including gastrointestinal disorders, autoimmune diseases, and mental health disorders.
Effects of inflammation on gut health
Inflammation in the gut can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiota, leading to dysbiosis and increased permeability of the intestinal lining, also known as “leaky gut.” This condition allows harmful substances like bacteria and toxins to enter the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and further inflammation. Chronic gut inflammation has been linked to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and even mood disorders like anxiety and depression.
How anti-inflammatory compounds in whole grains support gut health
The presence of anti-inflammatory compounds in whole grains can positively impact gut health. Research suggests that these compounds may help reduce gut inflammation, promote a balanced gut microbiota, and enhance the integrity of the intestinal barrier. By mitigating inflammation in the gut, whole grains can contribute to a healthier digestive system and overall well-being.
Fiber Content in Whole Grains
Role of dietary fiber in gut health
Dietary fiber, found in abundance in whole grains, is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. Instead, it passes through the digestive system relatively intact, providing various health benefits. Fiber serves as food for the beneficial bacteria in the gut, helping to maintain a diverse and balanced gut microbiota. It also adds bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
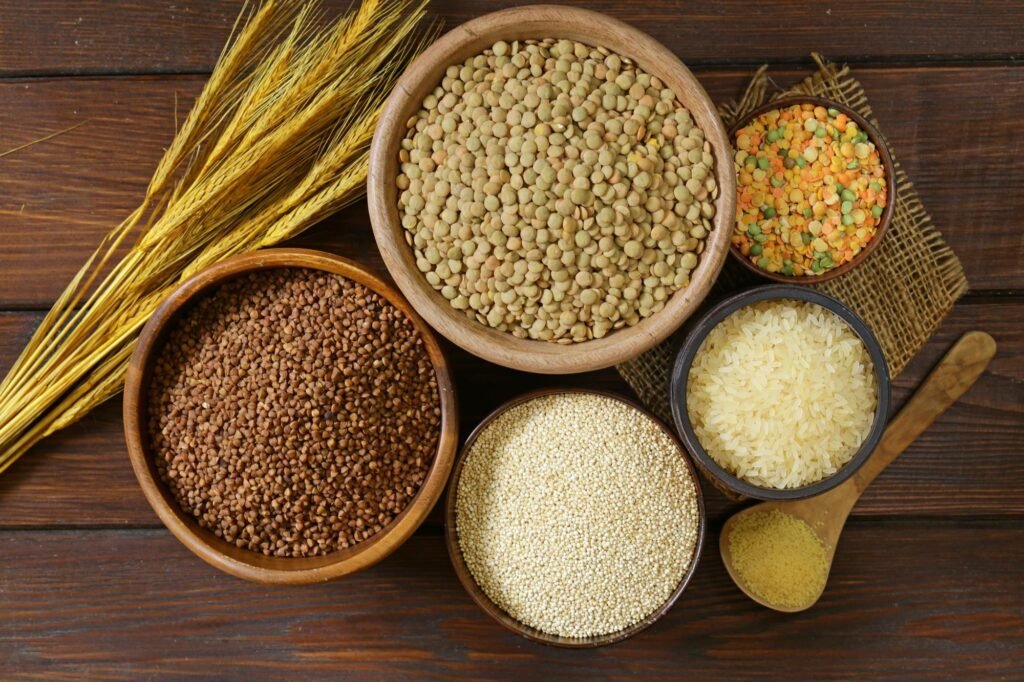
Amount of fiber in different whole grains
Different whole grains vary in their fiber content, but all contribute to the recommended daily intake of fiber. Here’s a general overview of the fiber content in some common whole grains:
- Wheat: Whole wheat flour contains approximately 12 grams of fiber per cup.
- Oats: A cup of cooked oats boasts around 4 grams of fiber.
- Barley: Cooked barley provides about 6 grams of fiber per cup.
- Brown rice: One cup of cooked brown rice contains roughly 4 grams of fiber.
- Quinoa: With approximately 5 grams of fiber per cooked cup, quinoa is a good source of fiber.
- Amaranth: Cooked amaranth delivers about 5 grams of fiber per cup.
- Buckwheat: A cup of cooked buckwheat offers around 4 grams of fiber.
- Millet: Cooked millet contains about 2 grams of fiber per cup.
- Rye: Whole rye flour contains roughly 14 grams of fiber per cup.
- Corn: One cup of yellow cornmeal has approximately 9 grams of fiber.
Effect of fiber on inflammation in the gut
The high fiber content of whole grains is believed to contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects in the gut. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing fuel for beneficial gut bacteria, which in turn produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). These SCFAs have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, nourish the cells lining the gut, and promote overall gut health. By incorporating fiber-rich whole grains into your diet, you can support a healthier gut and potentially reduce inflammation in the digestive system.

This image is property of cathe.com.
Specific Whole Grains and Their Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Wheat
Whole wheat contains various anti-inflammatory compounds, such as phenolic acids, lignans, and flavonoids. These compounds have been shown to have protective effects against chronic diseases associated with inflammation. However, it’s important to note that some individuals may have sensitivities or allergies to wheat, so it’s essential to choose whole grain alternatives if necessary.
Oats
Oats are renowned for their high fiber content, with a specific type of fiber called beta-glucan, which has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory effects. Beta-glucan has been shown to reduce markers of inflammation in the body and support gut health.
Barley
Barley is rich in antioxidants like phenolic acids and flavonoids, which possess anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have found that incorporating barley into the diet can help reduce inflammation and improve gut health.
Brown rice
Brown rice contains lignans, phenolic acids, and other bioactive compounds that have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects. Choosing brown rice over refined white rice can provide additional health benefits, including supporting gut health through its fiber content.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a complete protein source and contains anti-inflammatory compounds like flavonoids and phytoestrogens. These compounds contribute to its role in reducing inflammation and promoting gut health.
Amaranth
Amaranth is a gluten-free whole grain that contains bioactive compounds like ferulic acid, which has been found to possess anti-inflammatory effects. Including amaranth in your diet can add variety to your whole grain choices while supporting gut health.
Buckwheat
Despite its name, buckwheat is not related to wheat and is suitable for individuals with gluten sensitivities. It contains antioxidants like phenolic acids and flavonoids, which have been associated with reduced inflammation and improved gut health.
Millet
Millet is a nutrient-dense whole grain that can provide anti-inflammatory benefits. Research has shown that millet’s polyphenols and other bioactive compounds may help reduce inflammation and protect against chronic diseases.
Rye
Rye is a versatile whole grain that can be consumed in various forms, including bread and crackers. It contains lignans, antioxidants, and other bioactive compounds that contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties and potential benefits for gut health.
Corn
Corn, when consumed in its whole grain form, contains bioactive compounds like phenolic acids and flavonoids that have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory effects. It can be enjoyed in many ways, such as in cornmeal, popcorn, or tortillas, to add more whole grains to your diet.
Bioactive Compounds and Gut Health
Phytochemicals in whole grains
Whole grains contain various phytochemicals, which are natural compounds produced by plants that have been found to have health benefits. Many of these phytochemicals, such as phenolic acids, flavonoids, and lignans, have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can support gut health.
Effect of phytochemicals on gut health
Phytochemicals present in whole grains have been associated with improved gut health by reducing inflammation, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, and supporting the integrity of the gut barrier. These compounds can help maintain a balanced gut microbiota and contribute to overall gut health.
Overview of other bioactive compounds in whole grains
In addition to the previously mentioned bioactive compounds, whole grains contain other beneficial substances like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to their overall health-promoting properties. For example, vitamin E and selenium found in whole grains have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects that can support gut health.

This image is property of extension.oregonstate.edu.
The Role of Whole Grains in Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation and chronic diseases
Chronic inflammation is a driving force behind many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. By reducing inflammation in the body, whole grains can help mitigate the risk of developing these diseases and support overall health.
Research on whole grain consumption and inflammation
Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between whole grain consumption and inflammation. These studies consistently show that individuals who consume higher amounts of whole grains have lower levels of systemic inflammation markers. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms, it is clear that incorporating whole grains into your diet can play a role in reducing inflammation.
Mechanisms by which whole grains reduce inflammation
Whole grains contain a wide range of bioactive compounds and fiber that contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. These compounds can modulate inflammatory pathways, reduce oxidative stress, promote gut health, and have other positive effects on the body’s immune response. By addressing inflammation at multiple levels, whole grains can support a healthier inflammatory balance in the body.
Additional Factors Affecting Gut Health
Probiotics and their role in gut health
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can support gut health by promoting a diverse and balanced gut microbiota. Including probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut in conjunction with whole grains can further enhance the benefits for gut health. Probiotics can work in synergy with the anti-inflammatory compounds and fiber in whole grains, creating a harmonious environment in the gut.
Prebiotics and their effect on gut health
Prebiotics are types of dietary fiber that serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria. By including prebiotic-rich foods like onions, garlic, and asparagus in your diet, you can provide nourishment for the beneficial bacteria in your gut, helping to support their growth and overall gut health.
Combining whole grains with other gut-friendly foods
To maximize the benefits for gut health, it’s essential to combine whole grains with other gut-friendly foods. This includes incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fermented foods into your diet. By creating a well-rounded and diverse diet, you can support a healthy gut microbiota and overall gut health.

This image is property of megdejongnutrition.com.
Practical Tips to Incorporate Whole Grains for Gut Health
Choosing whole grain products
When shopping for whole grain products, look for labels that specifically state “whole grain” or “100% whole wheat.” Avoid products that contain refined grains or have added sugars and processed ingredients. Opt for whole grain bread, brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain cereals to incorporate into your meals.
Preparing whole grain meals
Experiment with different whole grains in your cooking and try new recipes to keep things interesting. Incorporate whole grains into meals by using them as a base for salads, stir-fries, and grain bowls. Prepare whole grain porridges, soups, and stews to enjoy their comforting and nutritious properties.
Recipe ideas for incorporating whole grains into a gut-healthy diet
Here are some recipe ideas to inspire you on your journey to incorporating whole grains into a gut-healthy diet:
- Overnight oats with berries and nuts
- Quinoa and vegetable stir-fry
- Barley and mushroom risotto
- Buckwheat pancakes with fresh fruit
- Whole grain wrap with lean protein, veggies, and avocado
- Spiced millet salad with roasted vegetables
- Rye bread with smoked salmon and avocado
- Corn tortilla tacos with grilled vegetables and salsa
- Amaranth porridge with cinnamon and mixed berries
Experiment with these recipes and adapt them to your taste preferences, adding other gut-friendly ingredients like fermented foods, leafy greens, and probiotic-rich toppings.
Conclusion
Incorporating whole grains into your diet can have a multitude of benefits for gut health. The anti-inflammatory compounds, fiber content, and other bioactive substances found in whole grains contribute to reducing inflammation, promoting a healthy gut microbiota, and supporting overall well-being. By choosing whole grain products, preparing whole grain meals, and combining them with other gut-friendly foods, you can reap the positive effects on gut health and potentially reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Remember the importance of a balanced diet and consider incorporating whole grains into your regular meals for optimal gut health and overall wellness.
This image is property of www.true-well.co.

