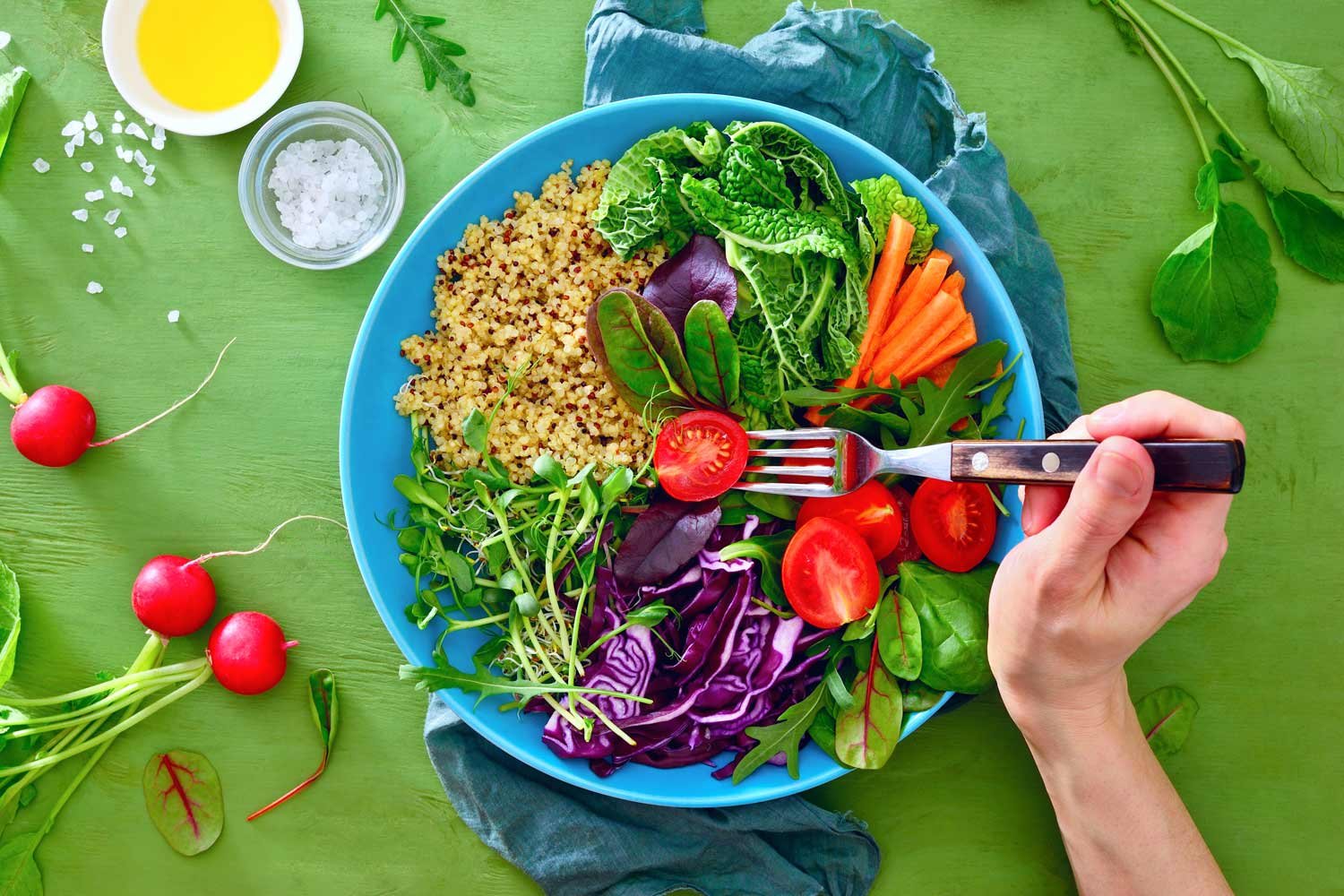
Did you know that what you eat can have an impact on your gut hormone regulation? It turns out that vegetables, those colorful and nutritious wonders, may play a significant role in balancing your body’s hormone levels. Recent research suggests that certain vegetables, such as broccoli and spinach, contain compounds that can stimulate the production of hormones that promote satiety and regulate blood sugar levels. So next time you’re at the grocery store, don’t forget to stock up on these hormone-friendly veggies and give your gut a boost!
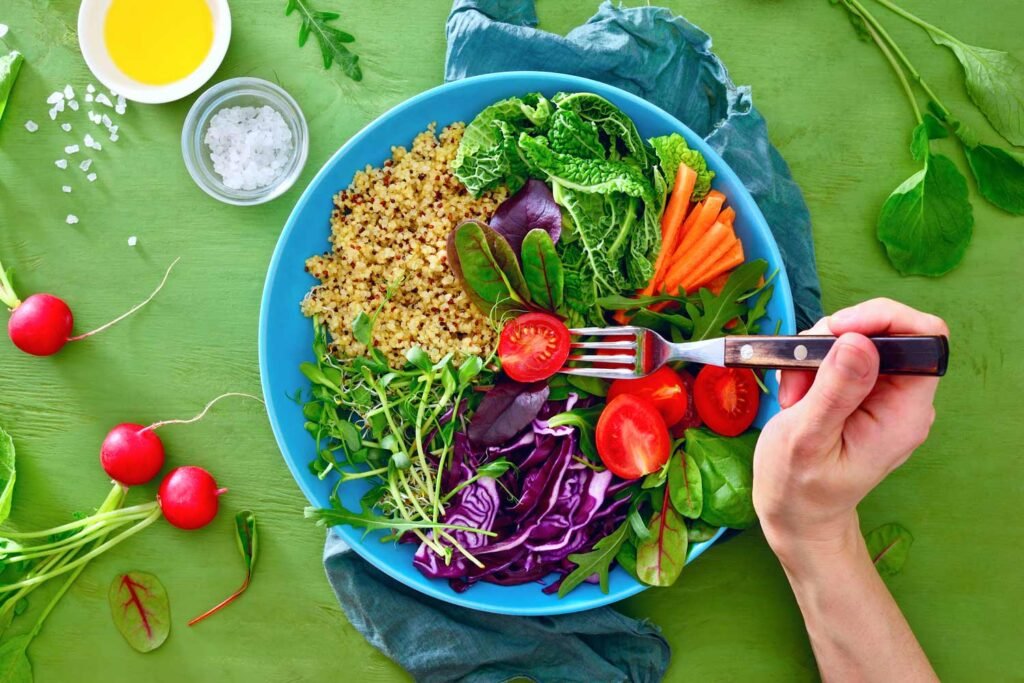

This image is property of www.mariongluckclinic.com.
Vegetables and Gut Health
The Importance of Gut Health
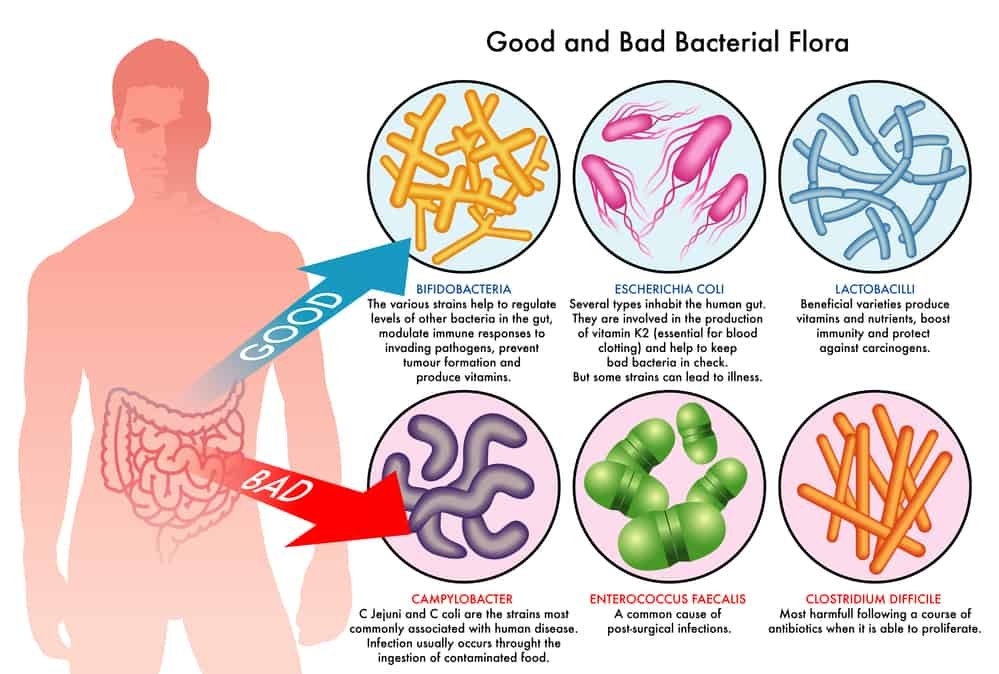
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being. The gut is home to trillions of beneficial bacteria that play a crucial role in digesting food, absorbing nutrients, and supporting our immune system. It is increasingly recognized that gut health is linked to various aspects of our health, including mental well-being, immunity, and even weight management.
The Role of Gut Hormone Regulation
Gut hormones are chemical messengers produced in the gastrointestinal tract that regulate various physiological functions, including appetite, metabolism, and energy balance. These hormones play a vital role in maintaining proper gut function and overall health. Imbalances in gut hormone regulation can contribute to conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and inflammatory bowel disease. Therefore, understanding the factors that influence gut hormone regulation is of great importance.
Types of Vegetables
Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, are rich in nutrients and known for their cancer-fighting properties. These vegetables are also high in fiber, which is essential for gut health. Consuming cruciferous vegetables can contribute to a healthy gut by promoting regular bowel movements and supporting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens, including spinach, kale, and Swiss chard, are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These vegetables are also an excellent source of fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain healthy gut bacteria. Leafy greens can be easily incorporated into your diet by adding them to salads, smoothies, or sautéing them as a side dish.
Root Vegetables
Root vegetables, such as carrots, beets, and sweet potatoes, are nutrient-dense and offer a wide range of health benefits. They are packed with fiber, which aids in digestion and supports gut health. Root vegetables also provide essential vitamins and minerals that are important for the overall functioning of the body. Incorporating these vegetables into your meals can help improve gut health and promote overall well-being.
Allium Vegetables
Allium vegetables, such as garlic, onions, and leeks, not only add flavor to your dishes but also offer numerous health benefits. These vegetables contain prebiotic fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria and promote a healthy gut environment. In addition, allium vegetables are known for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which can further support gut health.
Nightshade Vegetables
Nightshade vegetables, including tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants, are commonly consumed and offer a variety of nutrients. While some individuals may be sensitive to nightshade vegetables, they can be a healthy addition to a balanced diet for most people. These vegetables are rich in antioxidants and fiber, which can promote gut health and overall well-being.
Link Between Vegetables and Gut Hormone Regulation
Impact of Fiber
Fiber is an essential component of vegetables and plays a significant role in gut hormone regulation. The consumption of fiber-rich vegetables can positively impact gut hormone levels by promoting feelings of fullness, reducing appetite, and regulating blood sugar levels. Soluble fiber, which can be found in vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts, forms a gel-like substance when digested, slowing down the absorption of nutrients and promoting a feeling of satiety.
Effect of Phytochemicals
Phytochemicals are natural compounds found in vegetables that have been linked to various health benefits. Some phytochemicals have been shown to influence gut hormone release, potentially affecting appetite and metabolism. For example, the phytochemical sulforaphane, found in cruciferous vegetables, has been shown to increase the release of gut hormones that regulate appetite and food intake.
Prebiotic Properties
Certain vegetables, particularly those high in fiber, act as prebiotics, nourishing the beneficial bacteria in the gut. Prebiotics provide a food source for these bacteria, allowing them to thrive and support a healthy gut environment. This, in turn, can influence gut hormone regulation by promoting the release of hormones that regulate appetite and energy balance.
Fiber and Gut Hormone Regulation
Soluble vs Insoluble Fiber
Vegetables contain both soluble and insoluble fiber, each playing a unique role in gut health. Soluble fiber, found in vegetables like sweet potatoes and carrots, absorbs water and forms a gel-like substance in the gut. This gel-like substance slows down digestion, promotes feelings of fullness, and may contribute to the regulation of gut hormones. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, speeds up digestion and helps prevent constipation by adding bulk to the stool.
Impact of Fiber on Appetite
Fiber-rich vegetables can have a significant impact on appetite regulation. The consumption of vegetables high in fiber can increase feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake. This is due to the fact that fiber-rich foods take longer to chew and digest, leading to a slower release of gut hormones that signal fullness. Additionally, fiber adds bulk to the diet, promoting a feeling of satiety and reducing the likelihood of overeating.
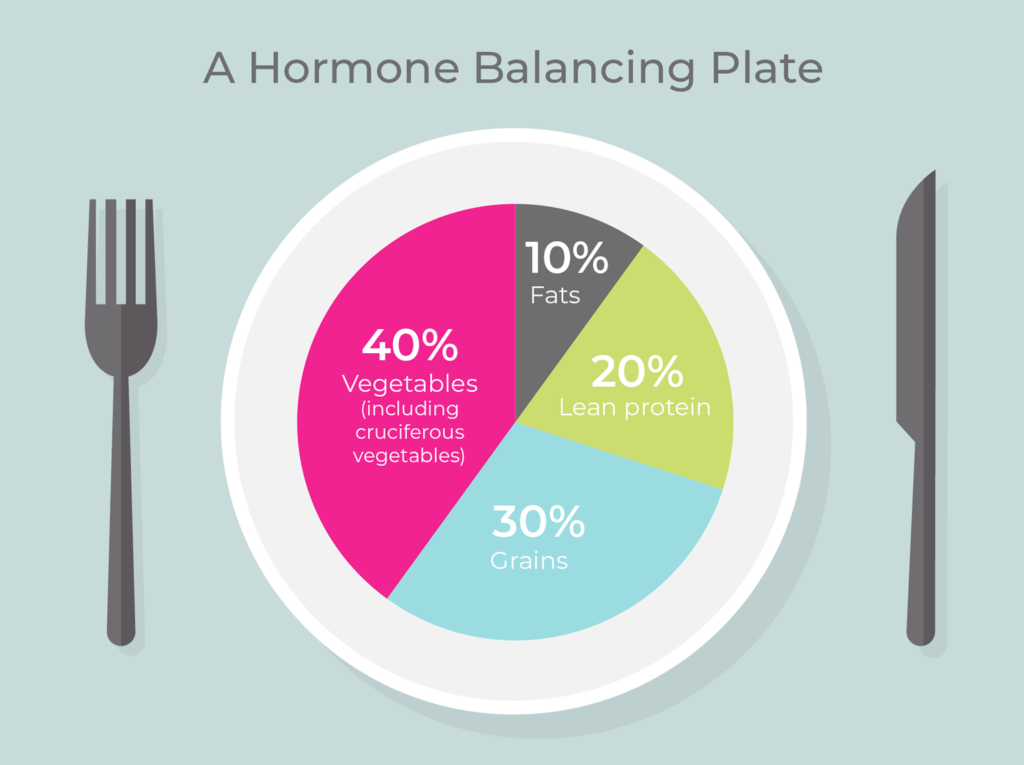
Effect of Fiber on Satiety Hormones
Gut hormones, such as leptin and ghrelin, play a crucial role in regulating appetite and satiety. Leptin, known as the “satiety hormone,” signals the brain when you have had enough to eat, while ghrelin, known as the “hunger hormone,” stimulates appetite. The consumption of fiber-rich vegetables can help regulate the release of these hormones, promoting feelings of fullness and reducing the urge to overeat.
This image is property of www.mariongluckclinic.com.
Phytochemicals and Gut Hormone Regulation
Antioxidant Properties
Phytochemicals found in vegetables, such as antioxidants, can have a positive impact on gut hormone regulation. Antioxidants help protect cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. By reducing oxidative stress in the body, antioxidants may help regulate gut hormone release and promote a healthy gut environment.
Potential Influence on Gut Hormone Release
Certain phytochemicals found in vegetables have been shown to influence gut hormone release. For example, the phytochemical capsaicin, found in chili peppers, has been found to increase the release of gut hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism. Similarly, the phytochemical quercetin, found in onions and apples, has been shown to affect gut hormone levels, potentially influencing appetite and food intake.
Prebiotics and Gut Hormone Regulation
Promoting Growth of Beneficial Gut Bacteria
Prebiotics found in vegetables serve as a food source for beneficial gut bacteria. These bacteria ferment prebiotics, producing short-chain fatty acids that serve as an energy source for the cells lining the gut. These short-chain fatty acids also play a role in gut hormone regulation, promoting the release of hormones that regulate appetite and energy balance.
Effect on Gut Hormone Secretion
The consumption of prebiotic-rich vegetables has been shown to influence gut hormone secretion. Studies have found that prebiotics can increase the release of gut hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY), which promote feelings of fullness and regulate appetite. This suggests that incorporating prebiotic-rich vegetables into your diet can have a positive impact on gut hormone regulation.

This image is property of sofreshnsogreen.com.
Gut Hormone Regulation and Weight Management
Leptin and Ghrelin
Leptin and ghrelin play a vital role in appetite regulation and energy balance. Leptin, produced by fat cells, signals the brain when you are full, while ghrelin, produced in the stomach, stimulates appetite. Imbalances in these hormones can contribute to weight gain and obesity. The consumption of vegetables, particularly those high in fiber and phytochemicals, can help regulate the release of these hormones, potentially aiding in weight management.
Effect of Gut Hormones on Metabolism
Gut hormones not only regulate appetite but also have the ability to influence metabolism. Certain gut hormones, such as GLP-1, have been shown to increase energy expenditure and fat oxidation, leading to potential weight loss. By promoting the release of these hormones, vegetables may have a positive impact on metabolism and overall weight management.
Potential Impact of Vegetables on Weight Loss
Incorporating a variety of vegetables into your diet can contribute to weight loss efforts. Vegetables are low in calories and high in fiber, which can help create a feeling of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, the impact of vegetables on gut hormone regulation may further support weight loss by promoting feelings of satiety and regulating metabolism.
Vegetable Diversity and Gut Hormone Regulation
The Importance of Variety
Consuming a variety of vegetables is essential for maximizing the benefits of gut hormone regulation. Different vegetables contain unique combinations of fiber, phytochemicals, and prebiotics. By incorporating a diverse range of vegetables into your diet, you can ensure a wide array of nutrients that may positively impact gut hormone regulation and overall gut health.
Different Vegetables, Different Effects
It’s important to note that different vegetables can have varying effects on gut hormone regulation. While all vegetables offer numerous health benefits, certain types may have a more significant impact on gut hormones than others. For example, cruciferous vegetables are high in fiber and phytochemicals that have been specifically linked to gut hormone regulation. By including a variety of vegetables in your diet, you can take advantage of the unique benefits each type has to offer.
This image is property of youholistic.com.
Cooking Methods and Gut Hormone Regulation
Raw vs Cooked Vegetables
Both raw and cooked vegetables have their own benefits when it comes to gut hormone regulation. Raw vegetables often retain more nutrients and enzymes, which can support optimal digestion and gut health. On the other hand, cooking certain vegetables can help break down tough fibers, making them easier to digest and potentially increasing the availability of certain nutrients. Incorporating a combination of raw and cooked vegetables into your diet can ensure a balance of nutrients and promote overall gut health.
Effect of Cooking on Nutrient Bioavailability
Cooking vegetables can impact the bioavailability of certain nutrients. For example, cooking tomatoes can increase the availability of the phytochemical lycopene, which has been linked to various health benefits. While cooking can alter the nutrient content of vegetables, it is important to note that certain nutrients, such as fiber and phytochemicals, are generally not affected by cooking. It is recommended to incorporate a mix of raw and cooked vegetables to ensure a variety of nutrient intake.
Cooking Vegetables for Optimal Gut Hormone Regulation
To maximize the benefits of gut hormone regulation, it is recommended to cook vegetables using methods that preserve nutrient content while enhancing digestion. Steaming, sautéing, and roasting vegetables are great cooking methods that can retain nutrients while making them easier to digest. Additionally, pairing cooked vegetables with sources of healthy fats can increase the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, further supporting gut health and nutrient utilization.
Conclusion
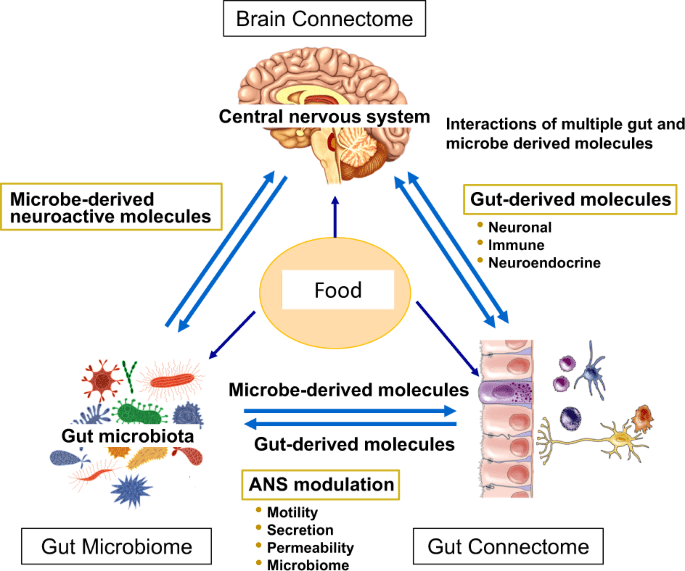
Vegetables play a vital role in supporting gut health and regulating gut hormones. The fiber, phytochemicals, and prebiotics found in vegetables have been shown to impact gut hormone release, appetite regulation, and weight management. By incorporating a variety of vegetables into your diet, both raw and cooked, you can optimize gut health and promote overall well-being. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms through which vegetables influence gut hormone regulation, but the existing evidence suggests that vegetables are indeed a key component of a healthy gut.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Further Research on Gut Hormone Regulation
As our understanding of gut health and hormone regulation continues to evolve, further research is needed to uncover the intricate mechanisms through which vegetables influence gut hormone release and overall gut health. Additionally, more studies are needed to explore the potential synergistic effects of different vegetables and their impact on gut hormone regulation. Further research in this area will help provide valuable insights into the role of vegetables in maintaining optimal gut health and promoting overall well-being.

