Have you ever wondered if the nuts and seeds you snack on have any effect on the regulation of your gut hormones? Well, you’re in for a tasty treat as we explore the potential impact of these crunchy delights on your digestion. In this article, we’ll examine the role of nuts and seeds in gut hormone regulation and uncover whether they can truly influence your overall gut health. So grab a handful of your favorite snack and let’s dig into this nutty exploration!
This image is property of cdnintech.com.
Role of Gut Hormones in Digestion and Metabolism
Overview of gut hormones
Gut hormones play a crucial role in the complex process of digestion and metabolism. These hormones are released by various cells in the gastrointestinal tract and are involved in regulating appetite, satiety, glucose and insulin regulation, and even influencing gut microbiota. Among the well-known gut hormones are ghrelin, peptide YY (PYY), glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and cholecystokinin (CCK). Understanding the role and regulation of these hormones is essential in comprehending the potential impact of nuts and seeds on gut hormone regulation.
Importance of gut hormone regulation
Gut hormone regulation is vital for maintaining proper digestive function and overall metabolic health. When gut hormones are dysregulated, it can lead to imbalances in appetite control, satiety signals, and glucose metabolism. This can contribute to the development of conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, exploring the factors that can influence gut hormone regulation, including diet and specific food components like nuts and seeds, is of significant importance in promoting optimal health.
Nutritional Profile of Nuts and Seeds
Macronutrient composition of nuts and seeds
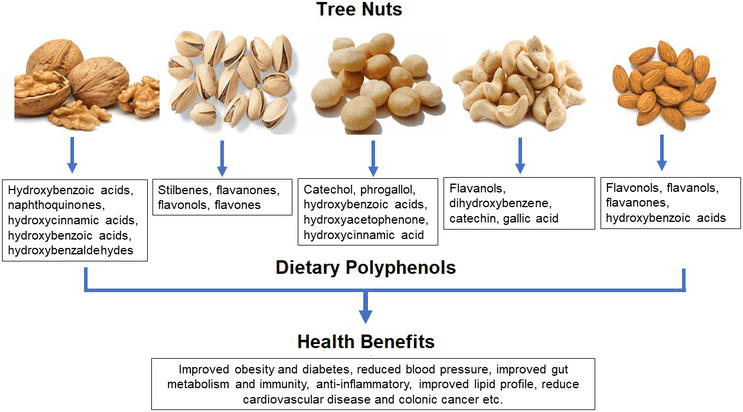
Nuts and seeds are rich sources of macronutrients, including healthy fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Although the precise macronutrient composition varies among different types of nuts and seeds, they generally contain a higher proportion of unsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health. Additionally, nuts and seeds offer a good plant-based protein source, making them an excellent option for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets. The presence of carbohydrates in these foods provides an energy source, while their fiber content contributes to digestive health.
Fiber content
One notable nutritional aspect of nuts and seeds is their high fiber content. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the human body cannot fully digest. Therefore, it passes through the digestive system relatively intact, providing several health benefits. The fiber found in nuts and seeds can help regulate bowel movements, improve satiety, and contribute to a healthy gut microbiota. By slowing down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, fiber also plays a role in blood sugar regulation.
Micronutrient content
In addition to their macronutrient composition, nuts and seeds are rich in essential micronutrients. These include vitamins, such as vitamin E, B vitamins, and minerals like magnesium, zinc, and iron. These micronutrients are important for various bodily functions, including enzyme activation, immune function, and antioxidant activity. By incorporating nuts and seeds into your diet, you can enhance your nutrient intake and support overall health and well-being.
Effects of Nuts and Seeds on Gut Hormones
Impact on appetite-regulating hormones
Research suggests that consuming nuts and seeds may influence appetite-regulating hormones. For example, some studies have shown that the consumption of nuts and seeds can decrease the levels of ghrelin, commonly known as the “hunger hormone.” Ghrelin stimulates appetite and promotes food intake, so a reduction in its levels may contribute to decreased hunger sensations and reduced calorie intake. Additionally, the presence of healthy fats in nuts and seeds can trigger the release of hormones like GLP-1 and PYY, which help promote feelings of fullness and satisfaction.
Effect on satiety hormones
In addition to influencing appetite-regulating hormones, nuts and seeds can also impact satiety hormones. Peptide YY (PYY) and cholecystokinin (CCK) are two hormones involved in signaling satiety, and studies have shown that the consumption of nuts and seeds can increase their release. These hormones send signals to the brain to indicate that you are full, helping to regulate food intake and prevent overeating. Therefore, including nuts and seeds in your diet can potentially contribute to better satiety control.
Influence on glucose and insulin regulation
Another area where nuts and seeds may have an impact is in glucose and insulin regulation. Many nuts and seeds have a low glycemic index, which means they have a minimal effect on blood sugar levels. This is attributed to their high fiber content and healthy fat composition. By slowing down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, nuts and seeds can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent rapid spikes and crashes. Additionally, the healthy fats in these foods may improve insulin sensitivity, facilitating better glucose utilization by the cells.
Fiber and Gut Hormone Regulation
Role of fiber in hormone release
Fiber plays a crucial role in hormone release within the gastrointestinal tract. The presence of fiber in the diet promotes the release of satiety hormones like PYY and CCK, which help regulate feelings of fullness and prevent overeating. One of the mechanisms through which fiber exerts this effect is by slowing down the emptying of the stomach, leading to prolonged satiety.
Effect of fiber on satiety signals
By increasing satiety signals, fiber can contribute to weight management by reducing overall calorie intake. When you consume foods rich in fiber, such as nuts and seeds, you are likely to feel satisfied for a more extended period, reducing the urge to snack or overeat. This effect can be particularly beneficial for individuals aiming to lose or maintain weight.
Fiber’s impact on gut microbiota
Fiber also plays a crucial role in shaping the composition of the gut microbiota, which refers to the trillions of microorganisms residing in our gastrointestinal tract. These microorganisms have been linked to various aspects of health, including metabolic regulation, immune function, and even mental well-being. The consumption of a fiber-rich diet, including nuts and seeds, provides a source of prebiotic fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria, leading to a healthier and more diverse microbiota.
This image is property of drhyman.com.
Micronutrients and Gut Hormones
Influence of vitamins and minerals on gut hormone regulation
Vitamins and minerals found in nuts and seeds have been found to exert influence on gut hormone regulation. For example, vitamin D has been associated with increased levels of PYY and GLP-1, two hormones involved in satiety regulation. Similarly, the mineral magnesium has been linked to improved insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation.
Effects of antioxidants on gut hormones
Nuts and seeds are also rich in antioxidants, which are compounds that protect cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Antioxidants, such as vitamin E and selenium, have been found to have beneficial effects on gut hormone regulation. These antioxidants may help reduce inflammation within the gut and improve gut hormone balance.
Specific micronutrients and hormone modulation
Certain specific micronutrients found in nuts and seeds have shown direct effects in modulating gut hormone levels. For example, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid present in flaxseeds and walnuts, has been found to increase levels of GLP-1, thereby promoting better glucose control and increased satiety. Additionally, the trace mineral zinc, which is abundant in pumpkin seeds, has been associated with the regulation of appetite-regulating hormones.
Gut Microbiota and Hormonal Regulation
Introduction to gut microbiota
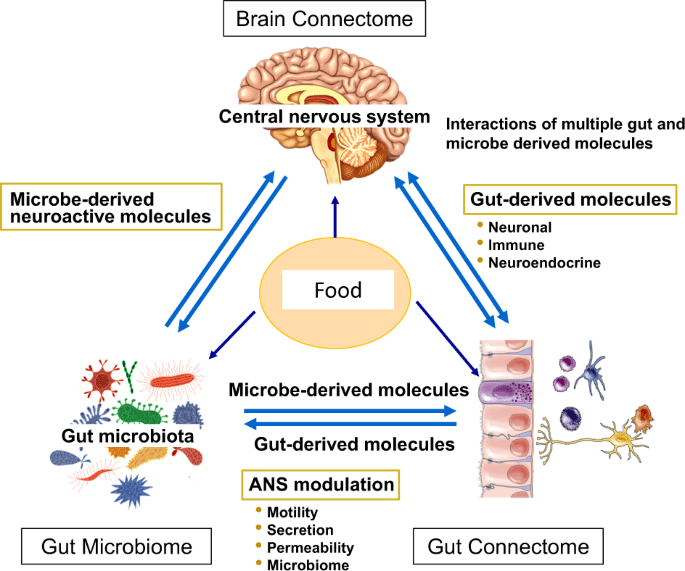
The gut microbiota refers to the diverse community of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract. These microorganisms play a crucial role in various aspects of health, including nutrient metabolism, immune function, and hormone regulation. A balanced and diverse gut microbiome is essential for optimal gut hormone regulation.
Interplay between gut microbiota and hormones
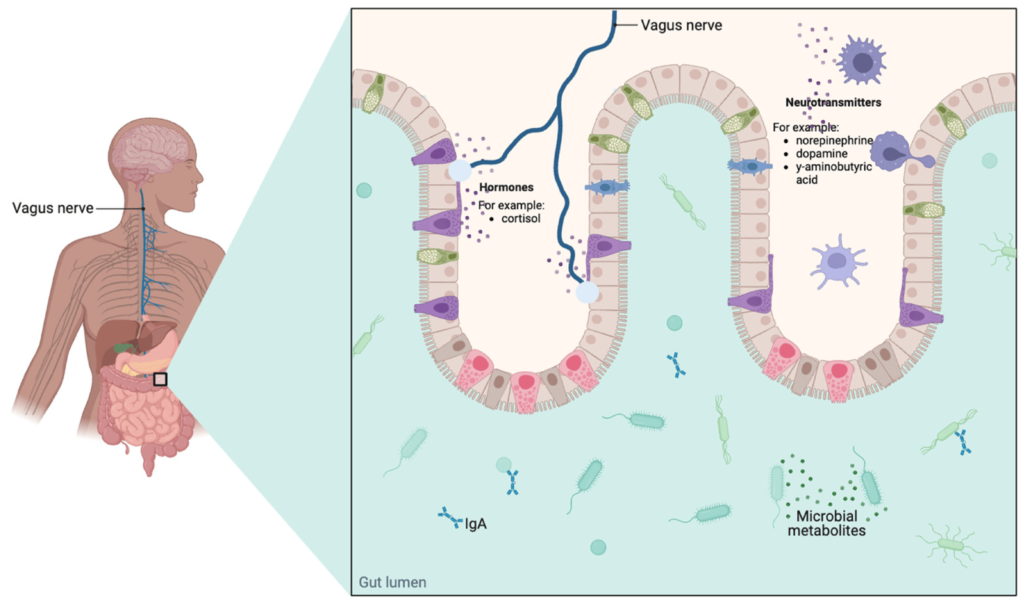
Emerging research suggests that the gut microbiota can directly influence gut hormone regulation. The gut microbiota produces metabolites that can interact with and influence the release of various hormones, including those involved in appetite regulation, glucose metabolism, and satiety. Moreover, alterations in the gut microbiota composition, such as dysbiosis or reduced diversity, may impact hormone regulation and contribute to metabolic disorders.
How nuts and seeds affect gut microbiota
Nuts and seeds, especially those high in fiber, can have a positive impact on gut microbiota composition. The fiber found in these foods serves as a substrate for beneficial bacteria, allowing them to thrive and produce beneficial metabolites. Additionally, the healthy fats and antioxidants in nuts and seeds may help reduce gut inflammation, promoting a healthier gut microbiota environment. By improving gut microbiota diversity and balance, nuts and seeds can indirectly contribute to better gut hormone regulation.
This image is property of pub.mdpi-res.com.
Clinical Studies and Findings
Research on nuts and hormone regulation
Several clinical studies have investigated the effects of nut consumption on gut hormone regulation. A study conducted on overweight and obese individuals found that incorporating almonds into their diet led to significant reductions in ghrelin levels and increased satiety hormone levels, such as PYY and CCK. Another study involving walnut consumption demonstrated an increase in GLP-1 levels, contributing to improved glucose control. These findings highlight the potential role of nuts in influencing gut hormone regulation.
Studies on seeds and gut hormones
Similarly, studies have explored the effects of seed consumption on gut hormone regulation. Chia seeds, for example, have been shown to increase PYY levels and decrease ghrelin levels, supporting appetite control. Flaxseeds, rich in ALA, have demonstrated an increase in GLP-1 levels, contributing to improved glucose control and increased satiety. These studies suggest that incorporating a variety of seeds into the diet can have positive effects on gut hormone regulation.
Potential Health Benefits of Nuts and Seeds
Weight management
The impact of nuts and seeds on gut hormone regulation suggests their potential role in weight management. By influencing appetite-regulating hormones, enhancing satiety, and controlling blood sugar levels, nuts and seeds can contribute to a healthy body weight. Additionally, the combination of healthy fats, protein, and fiber in these foods can help curb cravings and prevent overeating, promoting weight loss or maintenance.
Diabetes management
The ability of nuts and seeds to modulate glucose and insulin regulation holds promise for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By promoting better blood sugar control and improving insulin sensitivity, nuts and seeds can aid in managing and preventing type 2 diabetes. However, it is important to consider the overall dietary pattern and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable approach for diabetes management.
Cardiovascular health
The macronutrient composition of nuts and seeds, particularly their high content of unsaturated fats, makes them beneficial for cardiovascular health. These healthy fats can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, the presence of antioxidants, fiber, and minerals in nuts and seeds further contribute to cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, improving blood pressure, and supporting overall heart function.

This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Considerations and Recommendations
Portion control and moderation
While nuts and seeds offer numerous health benefits, it is important to exercise portion control and moderation due to their high calorie content. A recommended portion size is usually around 1 ounce, which is equivalent to a small handful. This allows you to enjoy the benefits of nuts and seeds without exceeding your daily calorie needs.
Variety in nut and seed consumption
To maximize the nutritional benefits, it is recommended to incorporate a variety of nuts and seeds into your diet. Different types of nuts and seeds offer unique combinations of nutrients, including various vitamins, minerals, and beneficial fats. By diversifying your intake, you can ensure a broader range of health-promoting compounds.
Individual differences and tolerances
Individuals may have different tolerances and sensitivities to nuts and seeds. Some people may be allergic to certain nuts or seeds, and others may experience digestive discomfort. It is important to be aware of your own tolerances and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or underlying health conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nuts and seeds have the potential to impact gut hormone regulation through various mechanisms. These nutrient-dense foods, rich in healthy fats, fiber, and essential micronutrients, can influence appetite-regulating hormones, promote satiety, and improve blood sugar control. Additionally, their beneficial effects on gut microbiota composition further contribute to optimal hormonal regulation. Incorporating a variety of nuts and seeds into your diet can potentially support weight management, diabetes management, and cardiovascular health. However, it is essential to practice portion control, include a variety of nuts and seeds, and consider individual differences and tolerances. Further research is needed to explore the full extent of the effects of nuts and seeds on gut hormone regulation and to continue uncovering their potential health benefits.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.

