In this article, you will explore the fascinating world of legumes and discover if they contain any anti-inflammatory compounds that can boost your gut health. Legumes have long been hailed as a nutritious and versatile food group, but their potential impact on inflammation and digestive well-being remains a topic of interest. By delving into the research and uncovering the various compounds found in legumes, you will gain a deeper understanding of how these legumes may hold the key to a healthier gut. So, join us as we explore the potential benefits of legumes on gut health and unravel the mysteries surrounding their anti-inflammatory properties.
Understanding Legumes
Definition of Legumes
Legumes are a group of plants that belong to the Fabaceae family and are known for their seed pods. These plants are widely cultivated for their edible seeds, which are commonly referred to as pulses. Legumes are rich in nutrients and are often considered a staple in vegetarian and vegan diets.
Common Types of Legumes
There are numerous types of legumes that are consumed around the world. Some examples include:
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Black beans
- Kidney beans
- Soybeans
These legumes vary in size, shape, and color, but they all share the common characteristic of being an excellent source of essential nutrients.
Nutritional Composition of Legumes
Legumes are packed with various essential nutrients that contribute to overall health. They are particularly known for their high protein content, making them a valuable source of plant-based protein for those following vegetarian or vegan diets. Legumes are also rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, including iron, magnesium, and folate. Additionally, legumes are generally low in fat and cholesterol, making them a healthy choice for maintaining a balanced diet.
Anti-inflammatory Compounds
What are Anti-inflammatory Compounds?
Anti-inflammatory compounds are substances that can help reduce inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to protect against injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues. Anti-inflammatory compounds work by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory substances in the body, helping to prevent or reduce inflammation.
Benefits of Anti-inflammatory Compounds
Consuming foods rich in anti-inflammatory compounds can have numerous benefits for overall health. These compounds have been linked to reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. They also play a crucial role in supporting immune function and promoting healthy aging.
Examples of Anti-inflammatory Compounds in Foods
Many plant-based foods, including legumes, contain natural anti-inflammatory compounds. Some notable examples include:
- Polyphenols: Found in foods like cherries, berries, and green tea, polyphenols have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel, as well as flaxseeds and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids are known for their potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Curcumin: A compound found in turmeric, curcumin has been widely studied for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Quercetin: Found in foods like onions, apples, and berries, quercetin is a flavonoid with powerful anti-inflammatory effects.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
Gut Health
Importance of Gut Health
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being. The gut, or gastrointestinal tract, is home to trillions of beneficial bacteria and other microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microorganisms play a vital role in various aspects of health, including digestion, immune function, and even mental health.
Factors Affecting Gut Health
Several factors can affect the health of the gut microbiota, including diet, lifestyle, medications, and even stress. A balanced diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics is crucial for promoting a healthy gut environment.
Link between Gut Health and Inflammation
Research suggests that there is a close connection between gut health and inflammation. A disruption in the balance of the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can lead to chronic inflammation in the gut. This inflammation can then spread throughout the body, contributing to the development of various chronic diseases.
Legumes and Gut Health
Fiber Content in Legumes
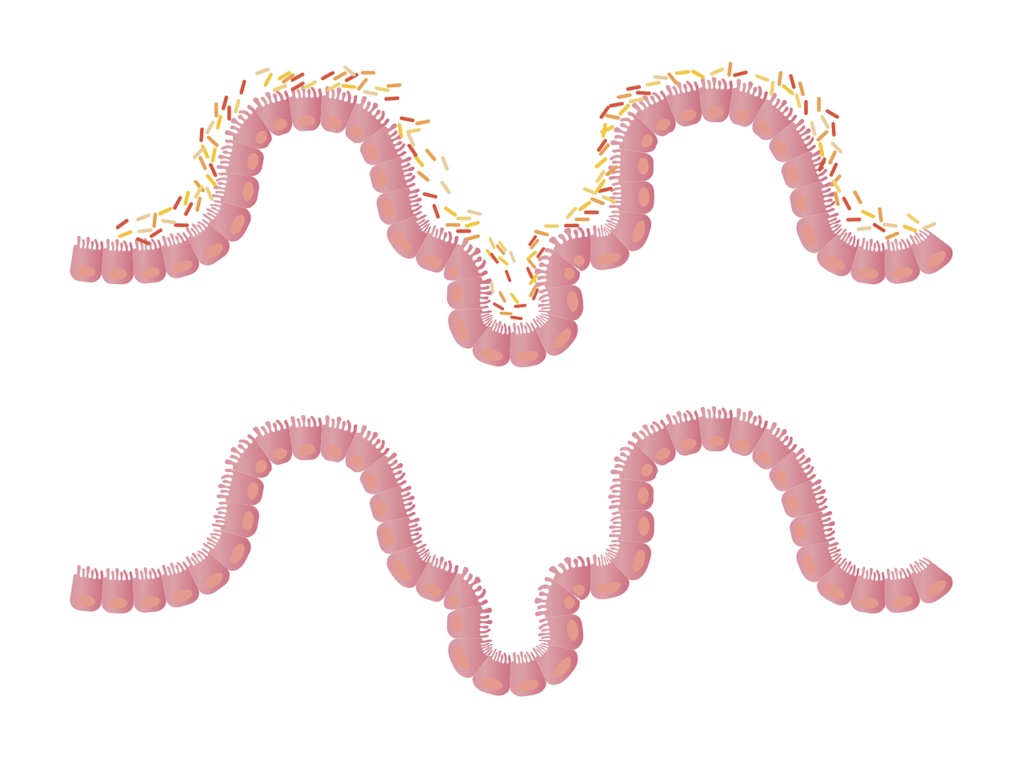
Legumes are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which can promote a healthy gut. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the human body and instead passes through the digestive system intact. This indigestible fiber serves as food for the beneficial bacteria in the gut, helping to maintain a diverse and thriving gut microbiota.
Role of Fiber in Gut Health
Fiber plays a crucial role in supporting gut health in several ways. Firstly, it helps regulate bowel movements, preventing constipation and promoting regularity. Secondly, fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment and stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Lastly, certain types of fiber can help reduce inflammation in the gut.
Effects of Legume Consumption on Gut Microbiota
Studies have shown that incorporating legumes into your diet can have a positive impact on gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. Legumes provide a good source of soluble and insoluble fibers, which can help enhance the diversity and abundance of the gut microbiota. This, in turn, may contribute to reduced inflammation and improved overall gut health.
This image is property of pixabay.com.
Specific Legumes and Anti-inflammatory Compounds
Soybeans
Soybeans are a versatile legume that contains various anti-inflammatory compounds. They are an excellent source of isoflavones, such as genistein and daidzein, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, soybeans are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which further contribute to their anti-inflammatory properties.
Lentils
Lentils are a nutrient-dense legume that contains a wide range of anti-inflammatory compounds. They are particularly high in polyphenols, which have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Lentils also provide a good source of dietary fiber, which can support gut health and overall well-being.
Chickpeas
Chickpeas, also known as garbanzo beans, are packed with anti-inflammatory compounds. They contain polyphenols, flavonoids, and other bioactive compounds that can help reduce inflammation in the body. Chickpeas are also an excellent source of fiber, making them a beneficial addition to a gut-healthy diet.
Black Beans
Black beans are another legume that offers numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory properties. They contain anthocyanins, which are powerful antioxidants known for their anti-inflammatory effects. Black beans are also high in fiber, protein, and other essential nutrients, making them an optimal choice for supporting overall health.
Kidney Beans
Kidney beans, like many other legumes, are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds. They contain flavonoids and other phytochemicals that have been shown to reduce inflammation in the body. Additionally, kidney beans provide a good source of dietary fiber, which can contribute to a healthy gut environment.
Evidence from Scientific Studies
Research on Legumes and Inflammation
Numerous scientific studies have investigated the relationship between legume consumption and inflammation. One study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that individuals who regularly consumed legumes had lower levels of inflammatory markers in their blood. Another study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology reported that legume consumption was associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
Studies on Legumes and Gut Health
Research has also explored the impact of legumes on gut health. A study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences found that regular consumption of legumes positively modulated the gut microbiota, leading to improved gut health. Another study published in the journal Nutrients demonstrated that legume consumption increased the production of short-chain fatty acids in the gut, which are beneficial compounds that support a healthy gut environment.
Findings and Conclusions
Overall, scientific evidence suggests that legumes contain anti-inflammatory compounds that can benefit gut health. Regular consumption of legumes has been associated with reduced inflammation and improved gut microbiota composition. However, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which legumes exert these beneficial effects.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
Other Health Benefits of Legumes
Protein Content in Legumes
Legumes are an excellent source of plant-based protein, making them an essential food for vegetarians, vegans, and those looking to reduce their consumption of animal products. Protein is essential for the growth and repair of tissues, as well as for the production of enzymes and hormones.
Nutrient-Dense Nature
Legumes are often referred to as a nutrient-dense food, meaning they provide a high concentration of essential nutrients compared to their calorie content. In addition to protein, legumes are rich in important vitamins and minerals, including folate, iron, magnesium, and potassium.
Potential Weight Management Benefits
Including legumes in your diet may also have potential benefits for weight management. Legumes are low in fat and high in fiber and protein, which can help promote feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, the combination of protein and fiber in legumes may help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the likelihood of overeating or cravings for sugary foods.
Incorporating Legumes into Diet
Tips for Cooking and Preparing Legumes
Cooking and preparing legumes can be easy and convenient with a few simple tips. Firstly, it is essential to soak dried legumes before cooking to help reduce cooking time and improve digestibility. Soaking can be done by placing the legumes in a large bowl of water overnight. Additionally, using a pressure cooker can significantly reduce cooking time. Adding spices and herbs during cooking can enhance the flavor of legumes and make them more enjoyable to eat.
Recipe Ideas with Legumes
There are countless delicious and nutritious recipes that incorporate legumes. Some popular options include:
- Chickpea curry
- Lentil soup
- Black bean tacos
- Kidney bean chili
- Soybean stir-fry
These recipes can be customized to suit various dietary preferences and can be a great way to introduce legumes into your diet.
Combining Legumes with Other Foods for Maximum Benefit
To maximize the nutritional and health benefits of legumes, it is beneficial to combine them with other foods. For example, pairing legumes with whole grains, such as brown rice or quinoa, creates a complete protein source. Adding vegetables to legume-based dishes helps increase the overall nutrient content and fiber intake. Additionally, consuming legumes with a source of vitamin C, such as citrus fruits or bell peppers, can enhance iron absorption from legumes.
Considerations and Precautions
Digestive Effects of Legumes
While legumes offer numerous health benefits, some individuals may experience digestive discomfort when consuming them. This is primarily due to the presence of complex carbohydrates called oligosaccharides, which can be difficult to digest for some people. Soaking or sprouting legumes, as well as gradually increasing their consumption, can help alleviate digestive issues.
Phytates and Lectins in Legumes
Legumes contain compounds known as phytates and lectins, which can bind to certain minerals and potentially interfere with their absorption. However, cooking legumes thoroughly and pairing them with other nutrient-rich foods can help mitigate the effects of phytates and lectins.
Individual Sensitivities and Allergies
Individuals with specific food sensitivities or allergies should approach legume consumption with caution. Allergies to legumes, especially peanuts, are relatively common and can cause severe allergic reactions. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect an allergy or intolerance to legumes.
Conclusion
Legumes, with their wide array of anti-inflammatory compounds and high fiber content, offer numerous health benefits, particularly for gut health. Incorporating legumes into your diet can help support a diverse and thriving gut microbiota, reduce inflammation, and potentially lower the risk of chronic diseases. Whether you enjoy lentil soup, chickpea curry, or a simple black bean salad, there are endless delicious and nutritious ways to incorporate legumes into your meals. So why not make legumes a regular part of your diet and reap the numerous health benefits they have to offer?


