If you’re looking to improve your digestive health, you may be wondering if nuts and seeds can lend a helping hand. Well, the answer might just surprise you. In this article, we’ll explore whether these tiny powerhouses can actually lower the risk of developing certain digestive disorders. So, grab a handful of your favorite nuts or sprinkle some seeds onto your salad, and let’s find out if they can truly be your gut’s best friends.
Overview of Digestive Disorders
Digestive disorders refer to a range of conditions that affect the digestive system, which includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. These disorders can lead to uncomfortable symptoms such as bloating, indigestion, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. They can also have a significant impact on overall health and quality of life. Understanding the definition of digestive disorders, common types, and risk factors can help you take proactive steps to maintain good digestive health.
Definition of Digestive Disorders
Digestive disorders are medical conditions that involve the malfunction or abnormal functioning of the digestive system. These disorders can arise from various causes, including lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition, certain medications, infections, and autoimmune diseases. They encompass a wide range of conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), celiac disease, and gallstones, among others.
Common Digestive Disorders
There are numerous digestive disorders that individuals may experience throughout their lives. Some of the most common ones include:
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): This condition occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn and acid reflux symptoms.
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a chronic disorder that affects the large intestine, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): IBD comprises conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
-
Celiac Disease: This autoimmune disorder occurs when the consumption of gluten triggers an immune reaction, damaging the lining of the small intestine.
-
Gallstones: Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, causing pain and discomfort, especially after consuming fatty foods.
Risk Factors for Digestive Disorders
Several factors can increase an individual’s risk of developing digestive disorders. These include:
-
Poor Diet: Eating a diet high in processed foods, sugar, unhealthy fats, and low in fiber can contribute to digestive problems.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can slow down digestion and lead to constipation and other digestive issues.
-
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can irritate the digestive system and increase the risk of various disorders.
-
Stress: High levels of stress can disrupt digestion and contribute to conditions such as ulcers and IBS.
-
Family History: Some digestive disorders, such as IBD, have a genetic component, so having a family history of these conditions can increase the likelihood of developing them.
Role of Diet in Digestive Health
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health. The foods we eat can either promote or harm the digestive system. Making healthy dietary choices can help prevent and manage various digestive disorders. By understanding the impact of diet on digestive disorders, the types of foods that benefit digestive health, and the importance of nutrients, you can take steps to improve your digestive well-being.
Impact of Diet on Digestive Disorders
A poor diet lacking in essential nutrients can contribute to the development of digestive disorders. Consuming processed foods high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and artificial additives can disrupt the natural balance of the gut microbiota and increase the risk of conditions such as GERD, IBS, and IBD. On the other hand, a balanced diet rich in fiber, plant-based foods, and lean proteins can support healthy digestion, reduce inflammation, and prevent digestive disorders.
Types of Foods That Can Benefit Digestive Health
Several types of foods have been found to promote digestive health:
-
Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber is essential for maintaining regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts and seeds are excellent sources of fiber.
-
Probiotic Foods: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can promote a healthy gut flora and aid digestion. Examples include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
-
Lean Proteins: Opting for lean sources of protein, such as fish, poultry, tofu, and legumes, provides the necessary amino acids for proper digestive function.
-
Healthy Fats: Including sources of healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish can help reduce inflammation in the digestive system.
Importance of Nutrients in Digestive Health
A well-balanced diet should provide essential nutrients that support overall digestive health. Some key nutrients include:
-
Vitamins and Minerals: Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds ensures an adequate intake of essential vitamins (such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and vitamin B12) and minerals (such as magnesium, zinc, and iron) that are vital for optimal digestive function.
-
Antioxidants: Antioxidants found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds help protect the digestive system from oxidative stress, which can contribute to the development of digestive disorders.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit the digestive tract.

This image is property of d2jx2rerrg6sh3.cloudfront.net.
Nuts and Seeds as a Source of Nutrition
Nuts and seeds are nutrient-dense foods that can provide a wide range of health benefits, including supporting digestive health. Here, we will explore the nutritional composition of nuts and seeds, their fiber and healthy fat content, and the vitamins and minerals they offer.
Nutritional Composition of Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are packed with essential nutrients that are beneficial for digestive health. They are excellent sources of plant-based protein, healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. While the specific nutritional composition will vary depending on the type of nut or seed, they all offer unique health benefits.
Rich in Fiber and Healthy Fats
Many nuts and seeds are rich in dietary fiber, which aids digestion and prevents constipation. Additionally, they provide a good source of healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and inflammation.
Vitamins and Minerals in Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are valuable sources of various vitamins and minerals necessary for proper digestive function. For example, almonds are rich in vitamin E, which has antioxidant properties that help protect cells in the digestive tract. Pumpkin seeds are high in zinc, which is essential for immune function, including the health of the gut lining. Incorporating a variety of nuts and seeds into your diet can provide a diverse array of micronutrients that support digestive health.
Effects of Nuts and Seeds on Digestive Disorders
Research suggests that nuts and seeds can have beneficial effects on digestive health and may even help lower the risk of certain digestive disorders. Let’s explore the studies linking nut and seed consumption to digestive health, the reduced risk of colon cancer, and the improvement in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms.
Studies Linking Nut and Seed Consumption to Digestive Health
Several studies have found associations between regular nut and seed consumption and improved digestive health outcomes. For example, a large-scale study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that individuals who consumed nuts at least five times a week had a significantly lower risk of developing digestive disorders compared to those who rarely consumed nuts.
Reduced Risk of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is one of the most common digestive cancers worldwide. Yet, several studies have suggested that regular nut and seed consumption may help decrease the risk of developing colon cancer. The high fiber content, antioxidants, and healthy fats in nuts and seeds are believed to contribute to this protective effect.
Improvement in Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Symptoms
While the precise causes of IBS remain unclear, certain dietary factors, including the intake of specific foods, can trigger symptoms in individuals with IBS. Nuts and seeds, when consumed in moderation, have been reported by many individuals with IBS to alleviate symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements. However, it is worth noting that individual responses can vary, and it is important to listen to your body and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.

This image is property of badgut.org.
Fiber Content and Digestive Health
Fiber plays a vital role in promoting healthy digestion and preventing various digestive disorders. Let’s explore the benefits of fiber, the high-fiber nuts and seeds, and how fiber helps prevent digestive disorders.
The Role of Fiber in Promoting Healthy Digestion
Dietary fiber, also known as roughage, is the indigestible part of plant foods that moves through the digestive system relatively intact. It adds bulk to the stool, softens it, and facilitates regular bowel movements. By promoting proper bowel function, fiber helps prevent constipation and can lower the risk of developing conditions such as hemorrhoids and diverticulosis.
High Fiber Nuts and Seeds
Several nuts and seeds are excellent sources of dietary fiber. For example, almonds pack a punch with approximately 3.5 grams of fiber per ounce, while chia seeds offer a whopping 10 grams of fiber per ounce. Incorporating these high-fiber nuts and seeds into your diet can increase your overall fiber intake and support healthy digestion.
How Fiber Helps Prevent Digestive Disorders
Fiber plays a crucial role in preventing digestive disorders by promoting regularity and ensuring proper functioning of the digestive system. Fiber-rich foods, such as nuts and seeds, can help prevent constipation, maintain a healthy gut microbiota, and reduce the risk of developing conditions like hemorrhoids, diverticulosis, and colon cancer. By adding more high-fiber nuts and seeds to your diet, you can support your digestive health and overall well-being.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Nuts and Seeds
Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to protect the body from injury and infection. However, chronic inflammation can contribute to various digestive disorders. The anti-inflammatory properties of nuts and seeds, primarily due to their beneficial omega-3 fatty acids, can aid in reducing inflammation in the digestive tract and promoting better digestive health.
Inflammation and Digestive Disorders
Chronic inflammation is believed to play a role in the development and progression of several digestive disorders, including IBD, IBS, and GERD. It can cause damage to the digestive tissues, disrupt the gut microbiota balance, and trigger symptoms. Avoiding pro-inflammatory foods and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as nuts and seeds, into the diet can help manage inflammation and decrease the risk of digestive disorders.
Beneficial Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are well-known for their healthy fat content, including omega-3 fatty acids. Walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, in particular, are excellent sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid. These omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce inflammatory markers in the body.
Reducing Inflammation in the Digestive Tract
Consuming nuts and seeds as part of a balanced diet can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. Omega-3 fatty acids have been found to decrease the production of pro-inflammatory molecules in the body, potentially mitigating inflammation in the gut. By incorporating these nutritious foods into your daily meals and snacks, you can support a healthier inflammatory response and improve digestive health.

This image is property of domf5oio6qrcr.cloudfront.net.
Probiotic Potential of Nuts and Seeds
Maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria, also known as gut flora, is essential for digestive health. Probiotics, often referred to as “good bacteria,” can support optimal digestion and reduce the risk of digestive disorders. Nuts and seeds can offer probiotic properties that contribute to a healthier gut microbiota and overall digestive well-being.
Importance of Healthy Gut Flora
The gut microbiota consists of trillions of bacteria that reside in the digestive tract. These bacteria fulfill several crucial roles, such as aiding in nutrient absorption, supporting the immune system, and maintaining a healthy gut lining. Imbalances in gut flora have been linked to various digestive disorders, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a diverse and thriving community of beneficial bacteria.
Probiotic Properties of Some Nuts and Seeds
While probiotics are commonly associated with fermented foods like yogurt and sauerkraut, certain nuts and seeds also offer probiotic potential. For example, almonds and pistachios contain prebiotic fibers that act as fuel for probiotics, thereby promoting their growth and activity in the gut. Some seeds, such as flaxseeds, are also believed to exhibit prebiotic properties, nourishing the beneficial bacteria in the digestive system.
Enhancing Digestive Health through Probiotics
Incorporating probiotic-rich foods, including nuts and seeds, into your diet can enhance digestive health by promoting a healthy balance of gut bacteria. These probiotic properties help support efficient digestion, nutrient absorption, and a robust immune system within the digestive tract. By including these nutritious foods alongside other probiotic sources, you can cultivate a healthy and thriving gut microbiota.
Choosing and Incorporating Nuts and Seeds in the Diet
To harness the potential benefits of nuts and seeds for digestive health, it is important to select fresh and quality sources, determine the recommended daily intake, and find creative ways to incorporate them into your meals and snacks.
Selecting Fresh and Quality Nuts and Seeds
When purchasing nuts and seeds, opt for fresh, unprocessed varieties to ensure optimal quality and nutrient content. Look for options that are free of added sugars, excessive salt, and artificial additives. It is also beneficial to store them properly in a cool, dry place to maintain their freshness and prevent spoilage.
Recommended Daily Intake
The recommended daily intake of nuts and seeds varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and overall calorie needs. As a general guideline, consuming a handful (about 1 ounce) of nuts and seeds per day can provide valuable nutrients and support digestive health. However, individual needs and dietary restrictions should be considered, so it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
Incorporating Nuts and Seeds into Meals and Snacks
There are countless delicious and creative ways to incorporate nuts and seeds into your meals and snacks. Here are a few ideas to get you started:
-
Breakfast: Sprinkle chia seeds or ground flaxseeds over your yogurt, oatmeal, or smoothie for an added boost of fiber and healthy fats.
-
Salads: Toss a handful of chopped nuts or toasted seeds, such as almonds or sunflower seeds, into your salad for added crunch and nutrition.
-
Trail Mixes: Create your own customized trail mix by combining a mix of nuts, seeds, and dried fruits for a convenient and satisfying snack.
-
Baking: Add chopped nuts or ground seeds, such as walnuts or flaxseeds, to your favorite baked goods, like muffins or bread, for both flavor and nutritional benefits.
-
Nut Butters: Enjoy natural nut butters, such as almond or peanut butter, as spreads on whole grain toast, apple slices, or celery sticks for a nutritious and delicious snack.
With a little creativity, you can incorporate nuts and seeds into various meals and snacks, reaping their nutritional benefits and supporting your digestive health.
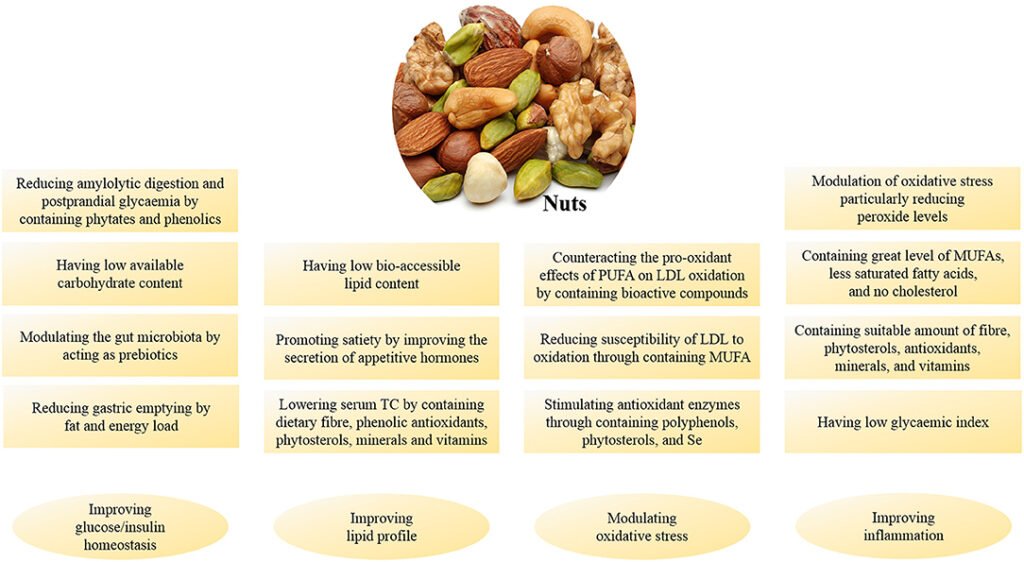
This image is property of www.frontiersin.org.
Precautions and Allergies for Nuts and Seeds
While nuts and seeds offer a myriad of potential benefits for digestive health, it is essential to be mindful of potential allergic reactions and individual sensitivities. It is always best to prioritize your health and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Potential Allergic Reactions
Nuts and seeds are considered common allergens, with allergic reactions ranging from mild to severe. Some individuals may have allergic reactions to certain nuts or seeds, such as peanuts, tree nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts), or sesame seeds. Symptoms can include itching, swelling, hives, difficulty breathing, or even anaphylaxis. If you have a known allergy to nuts or seeds, it is crucial to avoid them and seek appropriate medical advice.
Individual Sensitivities
While a true food allergy is an immune-mediated response, some individuals may experience sensitivities or intolerances to certain nuts or seeds. Symptoms may include digestive discomfort, bloating, gas, or diarrhea. If you suspect you have a sensitivity or intolerance, it is advisable to eliminate the suspected food temporarily and gradually reintroduce it while monitoring your body’s response. Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional can help you navigate any dietary challenges you may face.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you have specific health concerns, pre-existing medical conditions, or questions about incorporating nuts and seeds into your diet, it is always wise to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice based on your unique circumstances and help you make informed decisions about your digestive health and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nuts and seeds can play a beneficial role in supporting digestive health. Their rich nutritional composition, including fiber, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals, make them valuable additions to a balanced diet. Studies have shown associations between nut and seed consumption and reduced risks of certain digestive disorders, such as colon cancer and IBS symptoms. The fiber content promotes healthy digestion, while the anti-inflammatory properties can alleviate inflammation in the digestive tract. Additionally, nuts and seeds offer probiotic potential, supporting a diverse and thriving gut microbiota. However, it is important to be mindful of potential allergies or sensitivities and consult with a healthcare professional if necessary. By choosing fresh, quality sources and incorporating nuts and seeds into meals and snacks, you can harness their potential benefits for digestive health, enhancing your overall well-being. So go ahead and enjoy a handful of nuts and seeds each day to support your digestive system and improve your overall health!

This image is property of kimbralyrd.com.
