In the quest for a healthy gut, many people turn to plant-based foods. But how do legumes stack up against other options when it comes to gut health benefits? Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are known to be rich in fiber, protein, and various nutrients. In this article, we will explore the unique advantages that legumes bring to the table and how they measure up against other plant-based foods in terms of improving gut health. So, whether you’re a die-hard legume lover or just curious about their benefits, read on to discover how these humble seeds can play a significant role in nurturing your gut.
Nutritional Composition
Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are powerhouse foods when it comes to their nutritional composition. They are rich in fiber, protein, and complex carbohydrates, making them an excellent choice for promoting gut health. Additionally, legumes contain an array of vitamins and minerals that are essential for overall well-being.
Fiber Content
One of the standout features of legumes is their high fiber content. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the body. Instead, it passes through the digestive tract, providing numerous benefits along the way. Legumes are an excellent source of both soluble and insoluble fiber, which play different roles in the body.
Soluble fiber forms a gel-like substance in the gut, which slows down digestion and helps to maintain stable blood sugar levels. It also acts as a prebiotic, serving as food for beneficial gut bacteria. On the other hand, insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
Protein Content
Legumes are often referred to as the “meat of the poor” because they are an excellent source of plant-based protein. Protein is crucial for maintaining and repairing body tissues, including the cells lining our gut. A healthy gut lining is essential for preventing the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream and maintaining overall gut health.
In addition to being rich in protein, legumes also provide a good balance of essential amino acids. These are the building blocks of protein that our bodies cannot produce on their own. By consuming legumes, you ensure that your body receives all the necessary amino acids for optimal gut health.
Complex Carbohydrates
Unlike refined carbohydrates found in processed foods, legumes provide complex carbohydrates that are digested slowly, resulting in a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. This slow release helps to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent sudden spikes and crashes, which can negatively impact gut health.
Moreover, complex carbohydrates found in legumes act as a source of energy for our gut bacteria. When these carbohydrates reach the large intestine, they are fermented by gut bacteria, resulting in the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). These SCFAs play a vital role in maintaining a healthy gut environment.
Vitamins and Minerals
Legumes are packed with essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall gut health. B vitamins, such as folate and thiamin, play a crucial role in energy metabolism, ensuring that our gut cells have the energy they need to function optimally. Iron, another important mineral found in legumes, helps to maintain stool consistency and prevent conditions like constipation or diarrhea.
Zinc, yet another mineral abundant in legumes, plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier. This barrier acts as a protective layer, preventing harmful substances from entering the body. By consuming legumes, you can ensure an adequate intake of these vital vitamins and minerals, supporting your gut health.
Fiber and Digestive Health
Impact on Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota, a diverse community of microorganisms residing in our intestines, plays a crucial role in our overall health. The consumption of legumes, with their high fiber content, can contribute to a healthy and balanced gut microbiota. The soluble fiber in legumes acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial bacteria in the gut. This nourishment promotes their growth and activity, leading to a healthier gut microbiota.
Promotion of Regular Bowel Movements
Fiber is well-known for its role in promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Legumes, with their high fiber content, can help regulate bowel movements and maintain a healthy digestive system. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool, allowing it to move more easily through the intestines. Additionally, soluble fiber absorbs water, softening the stool and facilitating smooth elimination.
Reduced Risk of Digestive Disorders
The consumption of legumes has been associated with a reduced risk of various digestive disorders. Thanks to their fiber content, legumes can provide relief from conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and diverticulosis. The soluble fiber in legumes can help alleviate symptoms such as bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort. Including legumes in your diet may contribute to improved digestive health and a reduced risk of digestive disorders.
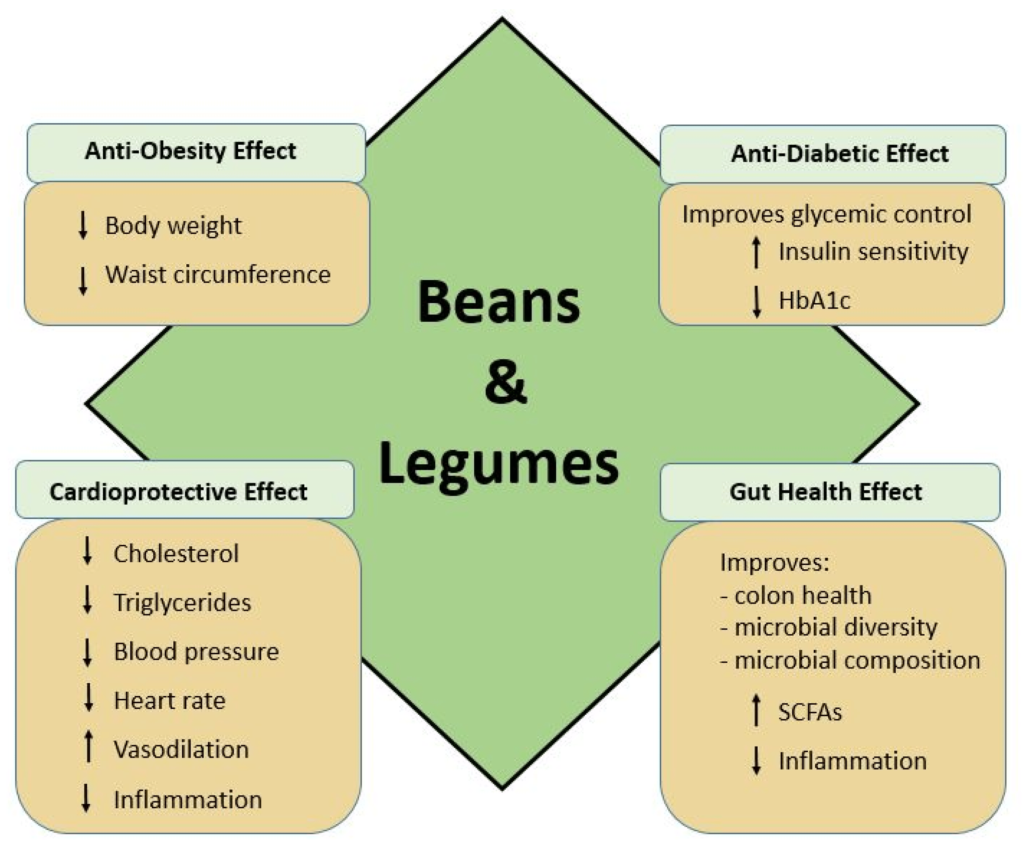
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Protein and Gut Health
Building Blocks for Gut Barrier
Protein is an essential nutrient for maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier. The cells that line our intestines are constantly being regenerated, and they require a sufficient amount of protein to do so effectively. By consuming legumes, you provide your body with plant-based protein, which can be utilized in the repair and maintenance of the gut barrier, preventing the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream.
Enhancement of Beneficial Gut Bacteria
A healthy gut is home to a diverse community of bacteria, and the consumption of legumes can contribute to their growth and activity. Legumes, with their protein content, act as a source of nutrients for beneficial gut bacteria. These bacteria play a crucial role in digestion and the production of certain vitamins, creating an optimal gut environment.
Immune Modulation
The gut plays a vital role in our immune system, and legumes can have a positive impact on immune modulation. Legumes contain compounds that can modulate immune responses, resulting in a balanced immune system. By including legumes in your diet, you may support overall gut health and reinforce your immune function.
Complex Carbohydrates and Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Fermentation by Gut Bacteria
Once the complex carbohydrates found in legumes reach the large intestine, they are fermented by gut bacteria. This fermentation process is essential for the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have numerous benefits for gut health. The fermentation of complex carbohydrates provides fuel for bacteria and promotes a healthy gut environment.
Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
The fermentation of complex carbohydrates found in legumes leads to the production of SCFAs, such as butyrate, propionate, and acetate. SCFAs provide a source of energy for the cells lining our intestines, promoting their health and function. Additionally, SCFAs have anti-inflammatory properties and play a role in maintaining a balanced gut microbiota.
Improved Colon Health
SCFAs have been shown to have a positive impact on colon health. The butyrate produced during the fermentation of complex carbohydrates acts as the main energy source for colon cells. This energy source helps to maintain the integrity of the colon lining, reducing the risk of conditions such as colon cancer. By consuming legumes, you can support colon health and contribute to a healthy gut environment.

This image is property of mybigfatgrainfreelife.com.
Vitamins and Minerals for Gut Health
B Vitamins and Energy Metabolism
Legumes are a rich source of B vitamins, including folate, thiamin, and niacin. These vitamins play a crucial role in energy metabolism, ensuring that our gut cells have the energy they need to function optimally. By including legumes in your diet, you can ensure an adequate intake of these essential vitamins, supporting overall gut health.
Iron and Stool Consistency
Iron is a mineral that is essential for various bodily functions, including maintaining stool consistency. Adequate iron intake can prevent conditions such as constipation or diarrhea, promoting a healthy digestive system. Legumes, with their iron content, can be a valuable addition to your diet to support optimal gut health.
Zinc and Gut Barrier Integrity
Zinc is a mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier. The gut barrier acts as a protective layer, preventing harmful substances from entering the body. By consuming legumes, you can ensure an adequate intake of zinc, supporting overall gut health and reinforcing the gut barrier.
Prebiotic Properties of Legumes
Effects on Gut Microbiota
Legumes possess prebiotic properties, meaning they promote the growth and activity of beneficial gut bacteria. The fibers present in legumes serve as a food source for these bacteria, allowing them to thrive and perform their essential functions. By consuming legumes, you can positively influence the composition and diversity of your gut microbiota.
Selective Promotion of Beneficial Bacteria
Different types of bacteria reside in our gut, and the consumption of legumes can selectively promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. The fibers present in legumes are broken down by specific bacteria in the gut, leading to the production of substances that benefit our health. The promotion of beneficial bacteria can contribute to a healthy gut environment and overall well-being.
Improved Digestion and Absorption
The prebiotic properties of legumes can improve digestion and nutrient absorption. By providing nourishment to beneficial gut bacteria, legumes support efficient digestion and enhance the absorption of nutrients from the foods we consume. Including legumes in your diet can result in improved digestive health and overall nutrient utilization.

This image is property of images-prod.healthline.com.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Reduction of Gut Inflammation
Inflammation in the gut can lead to various digestive disorders and compromise overall gut health. However, the consumption of legumes can help reduce gut inflammation due to their anti-inflammatory properties. The combination of fiber, antioxidants, and other bioactive compounds found in legumes contributes to their ability to mitigate inflammatory processes in the gut.
Decreased Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are characterized by chronic inflammation in the gut. Including legumes in your diet may help decrease the risk of developing these conditions. The anti-inflammatory effects of legumes can help maintain a balanced gut environment and reduce inflammation, potentially providing protection against inflammatory bowel diseases.
High Antioxidant Content
Protection against Oxidative Stress
Legumes are rich in antioxidants, which are compounds that protect our cells from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, leading to cellular damage. The antioxidants found in legumes, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, help neutralize free radicals and prevent gut cell damage.
Prevention of Gut Cell Damage
The high antioxidant content of legumes contributes to the prevention of gut cell damage. Gut cells are constantly exposed to various stressors, such as toxins and inflammation. By consuming legumes and their antioxidant compounds, you provide your gut cells with protection, supporting their health and overall gut well-being.

This image is property of images.everydayhealth.com.
Benefits for Weight Management
Increased Satiation and Reduced Caloric Intake
Legumes can be beneficial for weight management due to their high fiber and protein content. Fiber and protein are known to increase satiety, making you feel fuller for longer periods. By including legumes in your meals, you can reduce the overall caloric intake while still feeling satisfied, contributing to weight management efforts.
Regulation of Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and weight management. The slow digestion and complex carbohydrates found in legumes help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing sudden spikes and crashes. By including legumes in your diet, you can support stable blood sugar levels, providing benefits for weight management and overall health.
Whole Foods vs. Legume Derivatives
Synergistic Effects of Whole Legumes
While legume derivatives, such as flours and pastes, can be convenient for cooking and consumption, there are unique benefits to consuming whole legumes. Whole legumes provide the full range of nutrients, including fiber, protein, and vitamins, without any processing or additives. The synergy of these nutrients in their natural state contributes to optimal gut health and overall well-being.
Possible Downsides of Processed Legume Products
Although legume derivatives can be a convenient addition to meals, it is essential to be mindful of potential downsides. Some processed legume products, such as canned legumes or those with added sodium, may undermine the health benefits associated with whole legumes. Being aware of ingredient labels, opting for low-sodium options, and preparing meals with minimally processed legumes can help you maximize their gut health benefits.
In conclusion, legumes are a fantastic addition to a gut-healthy diet. Their high fiber content promotes regular bowel movements, supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, and reduces the risk of digestive disorders. Additionally, legumes provide essential protein, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to gut health and overall well-being. By incorporating legumes into your meals, you can enjoy the numerous benefits they offer for your gut, immune system, and weight management.
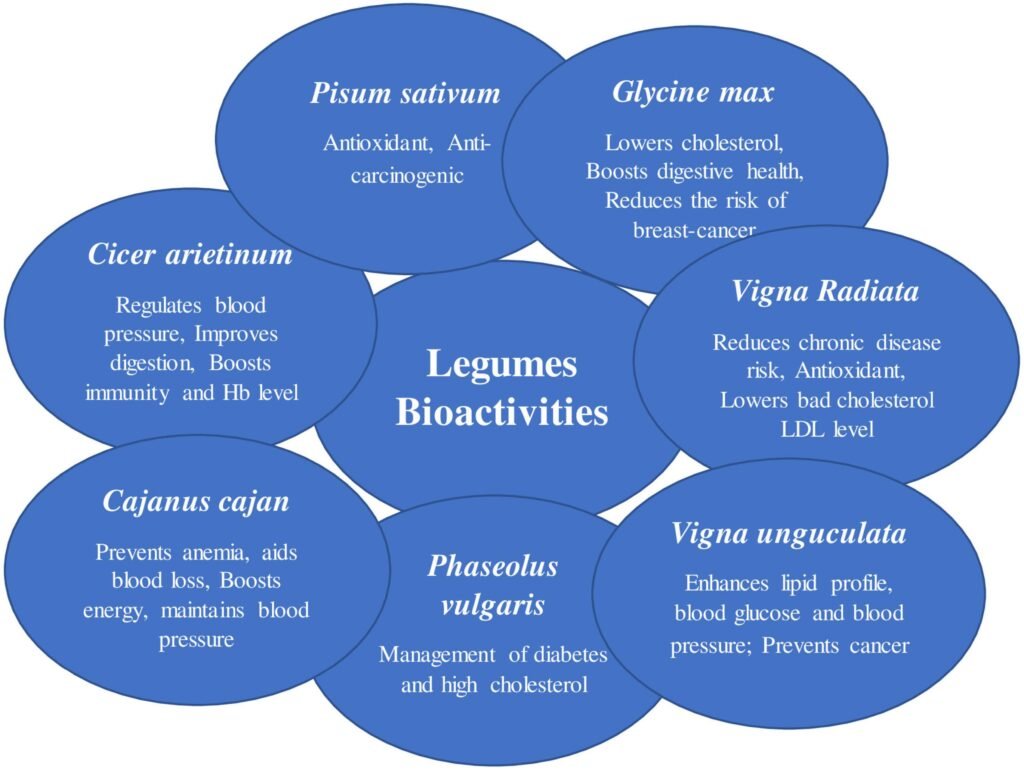
This image is property of www.frontiersin.org.

