Whole grains have long been hailed for their numerous health benefits, and one area where they truly shine is gut health. But how do whole grains stack up against other food groups when it comes to fostering a healthy gut? In this article, we will explore the unique advantages that whole grains offer in promoting gut health and compare them to other popular food groups to determine which ones reign supreme in supporting our digestive system. So grab a seat, and get ready to discover why incorporating whole grains into your diet is a must for optimal gut health!
Nutritional Composition
Fiber Content
Whole grains are a fantastic source of dietary fiber, an essential nutrient for maintaining good gut health. Fiber can be categorized into two types: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, promoting satiety and slowing down the absorption of nutrients, including sugar. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, adds bulk to stool and helps regulate bowel movements, preventing constipation. Whole grains contain both types of fiber, making them an excellent choice for promoting digestive health.
Vitamin and Mineral Content
Whole grains are a powerhouse of essential vitamins and minerals. They contain B vitamins like thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folate, which play a crucial role in energy metabolism and maintaining a healthy nervous system. Additionally, whole grains are rich in minerals such as iron, magnesium, and selenium, which are vital for various bodily functions. By incorporating whole grains into your diet, you can ensure that your body receives these important nutrients to support overall health.
Phytochemicals
Phytochemicals are natural compounds found in plant-based foods, and whole grains are no exception. These bioactive substances have been shown to exhibit a range of health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They may also have a role in reducing the risk of certain chronic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer. Whole grains, with their diverse array of phytochemicals, can contribute to an overall healthier body by providing protection against oxidative stress and inflammation.
Digestibility and Fermentation
Fiber Fermentation
The fiber found in whole grains is highly fermentable by the beneficial bacteria in our gut. During fermentation, the bacteria break down the fiber into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have numerous health benefits. SCFAs provide fuel for the cells lining the colon, promoting their health and integrity. Furthermore, SCFAs play a vital role in regulating the immune system and reducing inflammation in the gut.
Resistant Starch
Whole grains also contain resistant starch, a type of carbohydrate that resists digestion in the small intestine. Instead, it reaches the colon, where it serves as prebiotic, providing nourishment for the beneficial bacteria in our gut. These bacteria ferment resistant starch, producing SCFAs and other metabolites that contribute to gut health. By consuming whole grains, you can increase your intake of resistant starch and support a healthy gut microbiota.

This image is property of whataboutwheat.ca.
Microbiota Impact
Prebiotic Properties
Prebiotics are non-digestible carbohydrates that stimulate the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Whole grains, with their complex carbohydrates and fiber content, act as prebiotics and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli. These bacteria play a key role in maintaining gut health, supporting digestion, and enhancing the immune system. By incorporating whole grains into your diet, you can enjoy the prebiotic benefits they offer.
Microbial Diversity
A diverse gut microbiota is associated with better health outcomes. Whole grains, with their variety of nutrients and fibers, can contribute to microbial diversity in the gut. Consuming a range of whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat, ensures that you expose your gut to different types of fibers and nutrients, promoting the growth of a diverse range of beneficial bacteria. A diverse gut microbiota is linked to improved digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall well-being.
Inflammation and Disease Risk
Reduced Inflammatory Markers
Chronic inflammation has been implicated in the development of various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Whole grains have been shown to reduce inflammatory markers in the body, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These anti-inflammatory effects can help protect against chronic diseases and promote overall well-being.
Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases
Consuming whole grains as part of a balanced diet has been associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases. Studies have shown that individuals who regularly consume whole grains have a reduced risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some forms of cancer, particularly colon cancer. The combination of fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals found in whole grains may contribute to these protective effects and support long-term health.
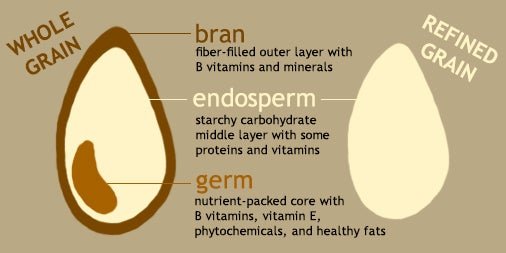
This image is property of www.hsph.harvard.edu.
Blood Sugar Control
Lower Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Whole grains, with their complex carbohydrates and fiber content, have a lower GI compared to refined grains. This means they have a gentler impact on blood sugar levels, helping to regulate glucose metabolism and prevent spikes in insulin. Including whole grains in your meals can support better blood sugar control, particularly for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin sensitivity refers to the ability of cells to respond to insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. Whole grains have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. By promoting more efficient glucose utilization, whole grains can help maintain balanced blood sugar levels and support overall metabolic health.
Weight Management
Feeling of Fullness
One of the benefits of whole grains is their ability to promote satiety, or the feeling of fullness. Whole grains take longer to digest due to their fiber content, which can help you feel satisfied for longer periods. This can be particularly beneficial for weight management, as it reduces the likelihood of overeating or snacking on unhealthy foods. By incorporating whole grains into your meals, you can support a healthy, balanced diet and maintain a healthy weight.
Positive Impact on Body Weight
Various studies have suggested that consuming whole grains is associated with a lower body mass index (BMI) and a reduced risk of obesity. The fiber content of whole grains, along with their low energy density, can contribute to weight management by providing bulk in the diet without adding excessive calories. Additionally, the nutrients and phytochemicals found in whole grains may have metabolic benefits that support a healthy body weight.

This image is property of wholegrainscouncil.org.
Heart Health
Lower LDL Cholesterol
High levels of LDL cholesterol are a risk factor for heart disease. Whole grains have been shown to lower LDL cholesterol levels, helping to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems. The combination of soluble fiber, plant sterols, and phytochemicals found in whole grains contributes to their cholesterol-lowering effects. By incorporating whole grains into a heart-healthy diet, you can support optimal cholesterol levels and maintain a healthy cardiovascular system.
Reduced Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is another significant risk factor for heart disease. Studies have shown that consuming whole grains can help lower blood pressure levels. The potassium, magnesium, and fiber found in whole grains may contribute to their blood pressure-lowering effects. By including whole grains in your diet, you can help maintain healthy blood pressure and support cardiovascular well-being.
Cancer Prevention
Protection Against Colon Cancer
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide. Fortunately, consuming whole grains has been associated with a reduced risk of developing colon cancer. The fiber content of whole grains promotes healthy bowel movements, reducing the time that potentially harmful substances are in contact with the colon lining. Additionally, the phytochemicals found in whole grains may have anti-cancer properties, further supporting colon health and reducing the risk of cancer.
Reduced Risk of Digestive Cancers
In addition to colon cancer, whole grains have also been linked to a reduced risk of other digestive cancers, such as gastric and esophageal cancer. The fiber and phytochemical content of whole grains may play a role in protecting against these types of cancers. By including whole grains in your diet, you can help protect your digestive system and reduce the risk of developing these potentially life-threatening diseases.

This image is property of media.post.rvohealth.io.
Digestive Health
Improved Bowel Regularity
Whole grains are well-known for their ability to promote bowel regularity and prevent constipation. The fiber content of whole grains adds bulk to stool, making it easier to pass through the digestive system. Additionally, the fermentation of fiber by beneficial gut bacteria produces SCFAs, which help regulate bowel movements and promote a healthy digestive tract. By consuming whole grains regularly, you can support optimal bowel regularity and ensure a healthy digestive system.
Reduced Constipation
Constipation is a common digestive issue that can cause discomfort and disrupt normal bowel movements. Including whole grains in your diet can help alleviate constipation by providing large amounts of fiber, promoting regularity, and softening stool. The combination of insoluble and soluble fiber found in whole grains contributes to their effectiveness in relieving constipation. By incorporating whole grains into your meals, you can support optimal digestive health and avoid the discomfort associated with constipation.
Overall Health Benefits
Improved Nutrient Absorption
The combination of fiber, vitamins, and minerals found in whole grains can enhance the absorption of nutrients from other foods. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which aids in nutrient absorption. Additionally, the presence of certain vitamins and minerals in whole grains can enhance the bioavailability of other nutrients. By including whole grains in your diet, you can maximize the absorption of essential nutrients and support overall health.
Enhanced Immune Function
The gut plays a crucial role in the immune system, and maintaining its health is essential for optimal immune function. Whole grains, with their prebiotic properties and beneficial impact on gut bacteria, can support a healthy immune system. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, whole grains contribute to a balanced gut microbiota, which in turn helps regulate immune responses and protect against infections and diseases. Including whole grains in your diet can provide a foundation for enhanced immune function and overall wellness.
In conclusion, whole grains offer a wide array of gut health benefits due to their nutritional composition, impact on digestion and fermentation, influence on the gut microbiota, and effects on various aspects of overall health. Including whole grains in your diet can promote optimal digestive health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, support weight management, improve heart health, help prevent cancer, enhance bowel regularity, and provide a range of other health benefits. By making whole grains a staple in your meals, you can reap the rewards of a healthier gut and enjoy the associated improvements in your well-being.
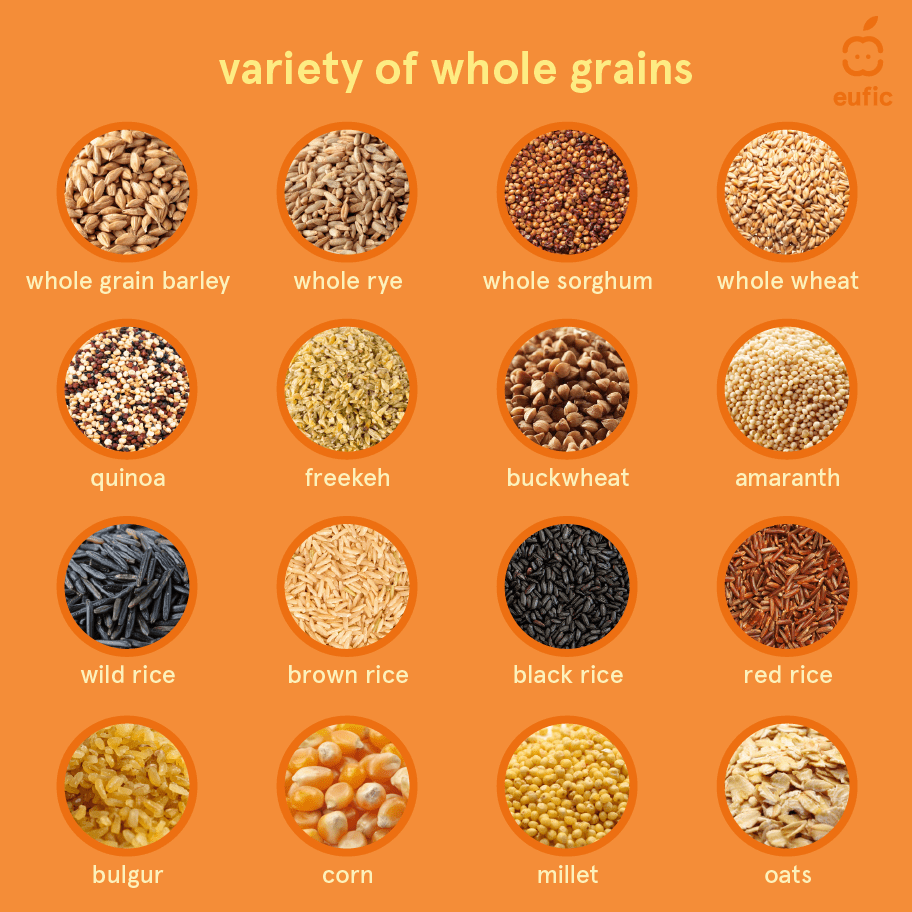
This image is property of www.eufic.org.

